radiography → radiografija
Radiography is nondestructive method of internal examination in which metal objects are exposed to a beam of X-ray or gamma radiation. Differences in thickness, density, or absorption caused by internal defects or inclusions are apparent in the shadow image produced on a fluorescent screen or photographic film placed behind the object.
reverse osmosis → reverzna osmoza
Reverse osmosis is the method used for obtaining freshwater from saltwater. The process uses a semi-permeable membrane through which pure water and not the salts will pass. The saltwater must be pressurised to approximately 25 bar, which makes it operationally expensive to produce large quantities of fresh water by this method.
chlorinity → klorinitet
Originally chlorinity (symbol Cl) was defined as the weight of chlorine in grams per kilogram of seawater after the bromides and iodides had been replaced by chlorides. To make the definition independent of atomic weights, chlorinity is now defined as 0.3285233 times the weight of silver equivalent to all the halides.
The Mohr-Knudsen titration method served oceanographers for more than 60 years to determine salinity from chlorinity. This modification of the Mohr method uses special volumetric glassware calibrated directly in chlorinity units. The Mohr method uses potassium chromate (K2CrO4) as an indicator in the titration of chloride ions chloride (plus a small amount of bromide and iodide) with a silver nitrate (AgNO3) standard solution.
The other halides present are similarly precipitated.
A problem in the Mohr titration was that silver nitrate is not well suited for a primary standard. The Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949) suggested that a standard seawater (Eau de mer Normale or Copenhagen Normal Water) be created and distributed to oceanographic laboratories throughout the world. This water was then used to standardize the silver nitrate solutions. In this way all chlorinity determinations were referred to one and the same standard which gave great internal consistency.
The relationship between chlorinity Cl and salinity S as set forth in Knudsen's tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
chromatography → kromatografija
Chromatography is a method of separation of the components of a sample in which the components are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary while the other moves. In gas chromatography, the gas moves over a liquid or solid stationary phase. In liquid chromatography, the liquid mixture moves through another liquid, a solid, or a gel. The mechanism of separation of components may be adsorption, differential solubility, ion-exchange, permeation, or other mechanisms.
sand filtration → pješčana filtracija
Sand filtration is a frequently used and very robust method of removing suspended solids from water. The filtration medium consists of a multiple layer of sand with a variety in size and specific gravity. Sand filters can be supplied in different sizes and materials, both hand operated and fully automatically.
toxic chemical → bojni otrov
Toxic chemical means any chemical which through its chemical action on life processes can cause death, temporary incapacitation, or permanent harm to humans or animals. This includes all such chemicals, regardless of their origin or of their method of production, and regardless of whether they are produced in facilities, in munitions or elsewhere.
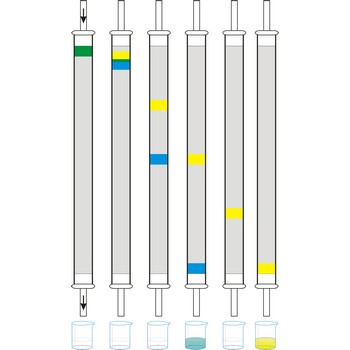
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
complexometry → kompleksometrija
Complexometry is a volumetric analytic method which is based on titration of metal ion solutions with a substance that, combined with metal ions yields complex compounds, e.g. EDTA. The stoichiometric ratio of EDTA-metal in complexometric analyses is always 1:1, whatever the valency of the metal
cryogenic fractionation → kriogena frakcinacija
Cryogenic fractionation is a process of separation of gases by cooling them until they enter their liquid state. Large scale gas production companies use this method to produce liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen etc. Gases have different boiling points (the temperature at which they change from liquid to gas). Oxygen has a boiling point of -183 °C, and nitrogen a boiling point of -195.8 °C. Therefore by cooling the gas mixture to -183 °C, the oxygen can be collected as liquid and the nitrogen remains its gaseous form.
experiment → eksperiment
Experiment is direct observation under controlled conditions. Most experiments involve carefully changing one variable and observing the effect on another variable (for example, changing temperature of a water sample and recording the change volume that results).
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Winklerova metoda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table