retardation factor → faktor zaostajanja
Retardation factor, RF, (in planar chromatography) is a ratio of the distance travelled by the centre of the spot to the distance simultaneously travelled by the mobile phase:
The RF value is characteristic for any given compound on the same stationary phase using the same mobile phase for development of the plates. Hence, known RF values can be compared to those of unknown substances to aid in their identifications.
solubility product constant → konstanta produkta topljivosti
Solubility product constant (Ksp) (or the solubility product) is the product of the molar concentrations of the constituent ions, each raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient in the equilibrium equation. For instance, if a compound AaBb is in equilibrium with its solution
the solubility product is given by
spin → spin
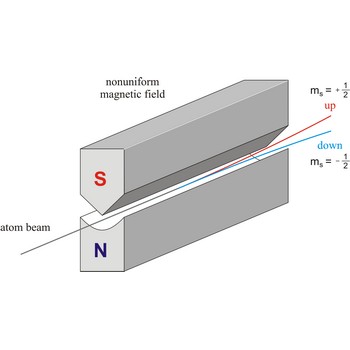
Spin is the intrinsic angular momentum of an elementary particle, or system of particles such as nucleus, that is also responsible for the magnetic moment; or, a particle or nucleus possessing such a spin. The spins of nuclei have characteristic fixed values. Pairs of neutrons and protons align to cancel out their spins, so that nuclei with an odd number of neutrons and/or protons will have a net non-zero rotational component characterized by a non-zero quantum nuclear spin number.
Stern-Gerlach experiment: a beam of silver atoms is split into two beams when it traverses a nonuniform magnetic field. Atoms with spin quantum number ms=+1/2 follow one trajectory, and those with ms=+1/2 follow another.
unified atomic mass unit → unificirana atomska jedinica mase
Unified atomic mass unit (u or mu) is a unit of mass used in atomic, molecular, and nuclear science, defined as the mass of one atom of 12C divided by 12. Its approximate value is
standard → standard
Standards are materials containing a known concentration of an analyte. They provide a reference to determine unknown concentrations or to calibrate analytical instruments.
The accuracy of an analytical measurement is how close a result comes to the true value. Determining the accuracy of a measurement usually requires calibration of the analytical method with a known standard. This is often done with standards of several concentrations to make a calibration or working curve.
A primary standard is a reagent that is extremely pure, stable, has no waters of hydration, and has a high molecular weight.
A secondary standard is a standard that is prepared in the laboratory for a specific analysis. It is usually standardised against a primary standard.
standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
universal indicator → univerzalni indikator
Universal indicator is an indicator which undergoes several colour changes over a wide range of pH. The colour is used to indicate pH directly. Universal indicators are usually mixtures of several indicators.
velocity → brzina
If a point-like object moves so that its position vector changes from being ri to rf, than the displacement Δr of object is
If a point-like object undergoes a displacement, Δr, in time Δt, its average velocity, v is defined as
The instantaneous velocity, v, is obtained from the average velocity by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average velocity approaches a limiting value, which is the velocity of a given instant:
Velocity is a vector quantity. If we plot the path of a moving particle as a curve in a coordinate system, the instantaneous velocity is always tangent to that curve.
SI unit for velocity is m s-1.
Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Rf-vrijednost." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table