magnetic permeability → magnetska permeabilnost
Magnetic permeability (μ), also called permeability, is a constant of proportionality that exists between magnetic induction and magnetic field intensity. This constant is equal to approximately μo = 1.257×10-6 H/m in a vacuum.
Magnetic permeability is often expressed in relative, rather than in absolute, terms. If μ represents the permeability of the substance in question, then the relative permeability, μr, is given by:
Nernst’s electrode potential equation → Nernstova jednadžba za elektrodni potencijal
For general reaction of some redox system
dependence of electrode potential of redox system upon activity of oxidised and reduced form in solution is described in Nernst’s equation for electrode potential:
where E = to electrode potential of redox system
E° = standard electrode potential of redox system
R = universal gas constant
T = thermodymical temperature
F = Faraday’s constant
z = number of electrons exchanged in redox reaction
aO = activity of oxidised form
aR = activity of reduced form
n = stechiometrical coefficient of oxidised form
m = stechiometrical coefficient of reduced form
Newton’s gravitational law → Newtonov zakon gravitacije
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force (gravitational force FG) directed along the line through centres of the two objects that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
m1 and m2 are masses of the two objects and r is the distance between them. G is universal constant of gravitation, which equals 6.67•10-26 N m2 kg-2. Strictly speaking, this law applies only to objects that can be considered pointlike object. Otherwise, the force has to be found by integrating the forces between various mass elements.
It is more properly to express Newton’s gravitational law by vector equation:
in which r1 and r2 are position vectors of masses m1 and m2.
Gravitational forces act on distance. Newton’s gravitational law is derived from Kepler’s law for planetary motion, using a physical assumption considering Sun as the centre and the source of gravitational force.
Additionally, every object moves in the direction of the force acting on it, with acceleration that is inversely proportional to the mass of object. For bodies on the surface of Earth, the distance r in gravitational law formula is practically equal to the Earth radius, RE. If the mass of the body on Earth surface is m and the mass of earth is ME, the gravitational force acting on that body can be expressed as:
where g is gravitational acceleration which is, although dependent on geographical latitude, usually considered as constant equal to 9.81 m s-2.
osmotic pressure → osmotski tlak
Osmotic pressure (Π) is the excess pressure necessary to maintain osmotic equilibrium between a solution and a pure solvent separated by a membrane permeable only to the solvent. In an ideal dilute solution
where cB is the amount-of-substance concentration of the solute, R is the molar gas constant, and T the temperature.
Ostwald’s dilution law → Ostwaldov zakon razrjeđenja
Ostwald’s dilution law is a relation for the concentration dependence of the molar conductivity Λ of an electrolyte solution, viz.
where c is the solute concentration, Kc is the equilibrium constant for dissociation of the solute, and L0 is the conductivity at cΛ = 0. The law was first put forward by the German chemist Wilhelm Ostwald (1853-1932).
resistivity → električna otpornost
Electrical resistivity, or specific resistance (ρ) is the electric field strength divided by the current density when there is no electromotive force in the conductor. Resistivity is an intrinsic property of a material. Materials with low resistivity are good conductors of electricity and materials with high resistivity are good insulators.
For a conductor of uniform cross section with area A and length L, and whose resistance is R, the resistivity is given by
The SI unit is Ω m.
salinity → salinitet
Salinity (S) is a measure of the quantity of dissolved salts in seawater. It is formally defined as the total amount of dissolved solids in seawater in parts per thousand (‰) by weight when all the carbonate has been converted to oxide, the bromide and iodide to chloride, and all organic matter is completely oxidized.
Chlorinity is the oldest of the salinity measures considered and is still a corner-stone in the study of dissolved material in seawater. Based on the principle of constant relative proportions it provides a measure of the total amount of dissolved material in seawater in terms of the concentration of halides. The relationship between chlorinity (Cl) and salinity as set forth in Knudsen’s tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Practical Salinity (SP) was introduced as a replacement for Chlorinity. Practical Salinity is is relatively easy to measure using standard conductometers, measurements are more precise and less time consuming than measurements of Chlorinity and accurate measurements can even be made in situ. Practical salinity SP is defined on the Practical Salinity Scale of 1978 (PSS-78) in terms of the conductivity ratio K15 which is the electrical conductivity of the sample at temperature t68 = 15 °C and pressure equal to one standard atmosphere, divided by the conductivity of a standard potassium chloride (KCl) solution at the same temperature and pressure. The mass fraction of KCl in the standard solution is 0.0324356 (32.4356 g of KCl in 1 kg of solution).
Note that Practical Salinity is a unit-less quantity. Though sometimes convenient, it is technically incorrect to quote Practical Salinity in "psu". For most purposes one can assume that the psu and the ‰, are synonymous.
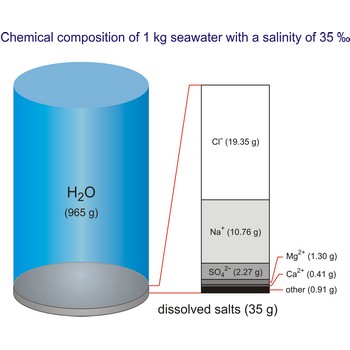
The global average salinity of ocean waters is about 35 ‰, that is, about 35 g of solid substances are dissolved in 1 kg of seawater.
seawater → more
Seawater is a complex mixture of 96.5 % water, 3.5 % salts, and smaller amounts of other substances, including dissolved inorganic and organic materials, particulates, and a few atmospheric gases. The world's oceans cover nearly 71 % (361 840 000 km2) of the Earth's surface (510 100 000 km2), with an average depth of 3 682.2 m.
The density of seawater is higher than that of fresh water because of its higher salinity. Seawater's freezing point is lower than that of pure water and its boiling point is higher. The average salinity of the ocean is 35 ‰, which means that for every kilograms of water, there are 35 g of salt. The relative abundance of the major salts in seawater are constant regardless of the ocean. Only six elements and compounds comprise about 99 % of sea salts: chlorine (Cl-), sodium (Na+), sulfur (SO42-), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), and potassium (K+).
Snell’s law → Snellov zakon
When a light ray comes on a boundary between two transparent media, it will be partly reflected and partly refracted. Both rays, reflected and refracted ray, lay in the plane of incidence. The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. The angle of refraction (Θ2) is related to the angle of incidence (Θ1) via Snell’s law:
where n1 and n2 are dimensionless constants - indexes of refraction of the two media.
Tafel plot → Tafelov dijagram
Tafel plot is the graph of the logarithm of the current density j against the overpotential η in electrochemistry in the high overpotential limit. An electrode when polarised frequently yields a current potential relationship over a region which can be approximated by:
where η is change in open circuit potential, i is the current density, B and i0 is constants. B is known as the Tafel Slope. If this behaviour is observed a plot of the semilogarithmic components is known as the Tafel line and the diagram is called the Tafel diagram.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Planckova konstanta." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table