acid → kiselina
Acid is a type of compound that contains hydrogen and dissociates in water to produce positive hydrogen ions. The reaction for an acid HA is commonly written:
In fact, the hydrogen ion (the proton) is solvated, and the complete reaction is:
This definition of acids comes from the Arrhenius theory. Such acids tend to be corrosive substances with a sharp taste, which turn litmus red and produce colour changes with other indicators. They are referred to as protonic acids and are classified into strong acids, which are almost completely dissociated in water, (e.g. sulphuric acid and hydrochloric acid), and weak acids, which are only partially dissociated (e.g. acetic acid and hydrogen sulphide). The strength of an acid depends on the extent to which it dissociates, and is measured by its dissociation constant.
In the Lowry-Brønsted theory of acids and bases (1923), the definition was extended to one in which an acid is a proton donor (a Brønsted acid), and a base is a proton acceptor (a Brønsted base). An important feature of the Lowry-Brønsted concept is that when an acid gives up a proton, a conjugate base is formed that is capable of accepting a proton.
Similarly, every base produces its conjugate acid as a result of accepting a proton.
For example, acetate ion is the conjugate base of acetic acid, and ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of ammonia.
As the acid of a conjugate acid/base pair becomes weaker, its conjugate base becomes stronger and vice versa.
A further extension of the idea of acids and bases was made in the Lewis theory. In this, a G. N. Lewis acid is a compound or atom that can accept a pair of electrons and a Lewis base is one that can donate an electron pair. This definition encompasses "traditional" acid-base reactions, but it also includes reactions that do not involve ions, e.g.
in which NH3 is the base (donor) and BCl3 the acid (acceptor).
air curtain → zračna zavjesa
Air curtain is a constant stream of bubbles provided by a submerged diffuser (usually a tube type), which surrounds a specified area.
amperometry → amperometrija
Amperometry is determining the concentration of a material in a sample by measuring electric current passing through a cell containing the solution.
azeotrope → azeotropi
Azeotrope is a mixture of two liquids that boils at constant composition, i.e. the composition of the vapour is the same as that of the liquid. Azeotropes occur because of deviations in Raoult’s law leading to a maximum or minimum in the boiling point - composition diagram. The composition of an azeotrope depends on the pressure.
Arrhenius equation → Arheniusova jednadžba
In 1889, Svante Arrhenius explained the variation of rate constants with temperature for several elementary reactions using the relationship
where the rate constant k is the total frequency of collisions between reaction molecules A times the fraction of collisions exp(-Ea/RT) that have an energy that exceeds a threshold activation energy Ea at a temperature of T (in kelvin). R is the universal gas constant.
balance → vaga
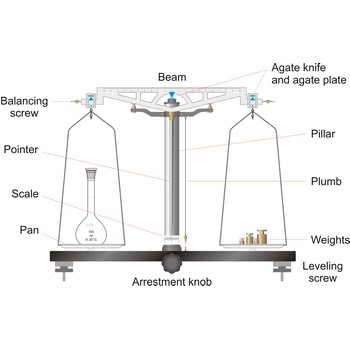
Balance is an instrument to measure the mass (or weight) of a body. Balance beam type scales are the oldest type and measure weight using a fulcrum or pivot and a lever with the unknown weight placed on one end of the lever, and a counterweight applied to the other end. When the lever is balanced, the unknown weight and the counterweight are equal. The equal-arm balance consists of two identical pans hung from either end of a centrally suspended beam. The unequal-arm balance is made with one arm of the balance much longer than the other.
More modern substitution balances use the substitution principle. In this calibrated weights are removed from the single lever arm to bring the single pan suspended from it into equilibrium with a fixed counter weight. The substitution balance is more accurate than the two-pan device and enables weighing to be carried out more rapidly.
Electromagnetic force restoration balances also use a lever system but a magnetic field is used to generate the force on the opposite end of the lever and balance out the unknown mass. The current used to drive the magnetic coil is proportional to the mass of the object placed on the platform.
Boltzmann equation → Boltzmannova jednadžba
Boltzmann equation is a statistical definition of entropy, given by
where S and k are the entropy and Boltzmann’s constant, respectively, and W is the probability of finding the system in a particular state.
coherence → koherentnost
If two overlapping light waves are to interfere detectably, the phase difference between them must remain constant with time, i.e. the waves must be coherent.
covalentity → kovalentnost
Covalentity is a maximum number of covalent bond that one atom can make, it is equal to the number of hydrogen atoms that are combined with other atoms. It is usually constant.
bomb calorimeter → kalorimetrijska bomba
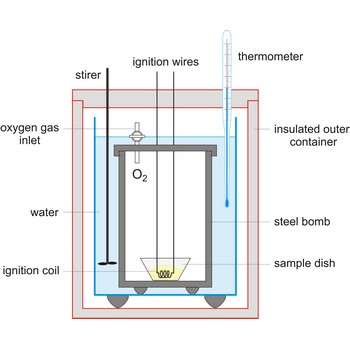
Bomb calorimeter is a type of constant-volume calorimeter used in measuring the heat of combustion of samples which can be burned in oxygen. Four essential parts are required in any bomb calorimeter:
- a bomb or vessel in which the combustible charges can be burned,
- a bucket or container for holding the bomb in a measured quantity of water, together with a stirring mechanism,
- an insulating jacket to protect the bucket from transient thermal stresses during the combustion process, and
- a thermometer or other sensor for measuring temperature changes within the bucket.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Planckova konstanta." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table