titar → titar
Titar (T) is a mass of titrated matter which is equivalent to 1 cm3 of solution. It is shown as T = 2.356 mg HCl / 1.0 cm3 NaOH, 0.1000 moldm-3, and it is usually shown in a table form. If the concentration of used standard solution (c) differs from one outlined in the table data (c0), the factor of correction (f) is induced
Titar is usually used in industrial operational laboratories where from titar tables mass or percentage of the ingredient in question is directly read.
transition metal → prijelazni element
This group of metals is distinguished from other metals not by their physical properties, but by their electronic structure. Transition metals are elements characterized by a partially filled d subshell. The First Transition Series comprises scandium (Sc), titanium (Ti), vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni) and copper (Cu). The Second and Third Transition Series include the lanthanides and actinides, respectively.
The transition metals are noted for their variability in oxidation state. Thus, manganese has two electrons in its outside shell and five electrons in the next shell down, and exhibits oxidation states of +1, +2, +3, +4, +5, +6, and +7.
They are also characterised by the fact that well into the series, going from left to right, the properties of the succeeding metals do not differ greatly from the preceding ones.
unununium → unununij
Unununium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in December 1994. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as unununium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. In bombardments of 209Bi targets with 64Ni using the velocity selector SHIP facility to discriminate in favor of the fused product, 272111 + 1n, three sets of localized alpha-decay chains were observed with position-sensitive detectors.
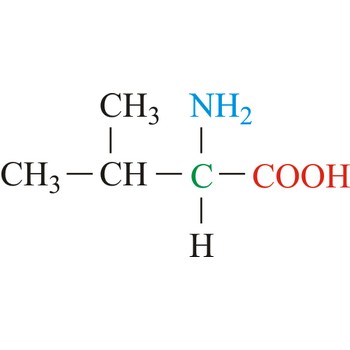
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
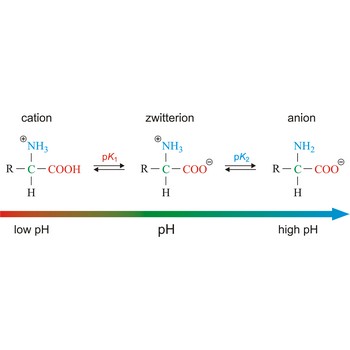
zwitterion → dipolarni ion
Zwitterion, also known as inner salt or dipolar ion, is an ion with a positive and a negative electrical charge at different locations within a molecule. As the molecule contains two opposite charges, it is electrically neutral. The term zwitterion is derived from the German word zwitter, meaning a hybrid, hermaphrodite. Zwitterions can be formed from compounds that contain both acid groups and base groups in their molecules (ampholytes).
All of the common amino acids found in proteins are ampholytes because they contain a carboxyl group (-COOH) that acts as an acid and an amino group (-NH2) that acts as a base. In the solid state, amino acids exist in the dipolar or zwitterion form. If acid is added to a solution containing the zwitterion, the carboxylate group captures a hydrogen (H+) ion, and the amino acid becomes positively charged. If base is added, ion removal of the H+ ion from the amino group of the zwitterion produces a negatively charged amino acid.
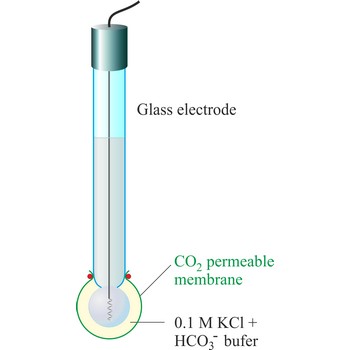
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Neutral face meme." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table