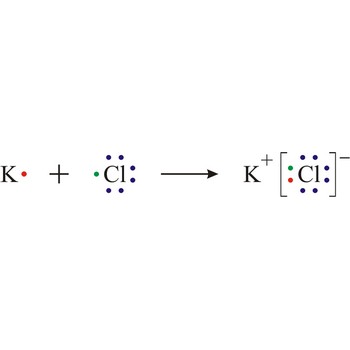Lewis base → Lewisova baza
Lewis base is an agent capable of donating a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Bronsted base → Bronstedova baza
Brønsted base is a material that accepts hydrogen ions in a chemical reaction.
base → baza
Historically, base is a substance that yields an OH - ion when it dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH>7. In the Brønsted definition, a base is a substance capable of accepting a proton in any type of reaction. The more general definition, due to G.N. Lewis, classifies any chemical species capable of donating an electron pair as a base. Typically, bases are metal oxides, hydroxides, or compounds (such as ammonia) that give hydroxide ions in aqueous solution.
conjugated base → konjugirana baza
Conjugated base is a particle which is left after a molecule of acid releases a proton.
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Lewis number → Lewisova značajka
Lewis number (Le) is a dimensionless quantity used in fluid mechanics, defined by
where a is thermal diffusivity and D is diffusion coefficient.
Schiff base → Schiffova baza
Schiff base is a class of compounds derived by the chemical reaction (condensation) of aldehydes or ketones with aromatic amines, for example
They were named after the German chemist Hugo Schiff (1834-1915).
weak base → slaba baza
Weak base is a base that only partially dissociates into ions in solution. Weak bases are weak electrolytes. Ammonia is an example of a weak base
Lewis structure → Lewisova struktura
Lewis structure is the representation of the electron arrangement in atoms, ions, or molecules by showing the valence electrons as dots placed around the symbols for the elements.
acid-base indicator → kiselo-bazni indikator
Acid-base indicator is a weak acid or weak base, such as litmus, methyl orange or phenolphthalein, which changes colour when it gains or loses an H+ ion.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Lewisova baza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table