derivative → derivat
Derivative is a compound that is derived from some other compound and usually maintains its general structure, e.g. trichlormethane (chloroform) is a derivative of methane.
glass → staklo
Glass is a brittle transparent solid with the molecular structure of a liquid. It is made by fusing together sand (SiO2), soda (Na2CO3), and lime (CaCO3) with small quantities other compounds. It is used for window panes and mirrors, for articles of table and culinary use, for lenses, and various articles of ornament.
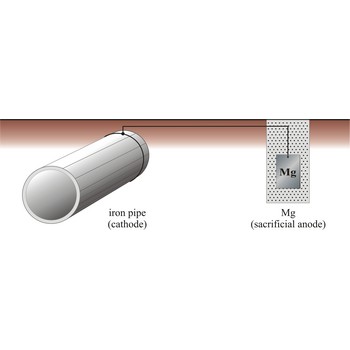
cathodic protection → katodna zaštita
Cathodic protection is a process in which a structural metal, such as iron, is protected from corrosion by connecting it to a metal that has a more negative reduction half-cell potential, which now corrodes instead of iron. There are two major variations of the cathodic method of corrosion protection. The first is called the impressed current method, and the other is called the sacrificial anode method.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
glycosyl group → glikozidna skupina
The structure obtained by removing the hydroxy group from the hemiacetal function of a monosaccharide.
groundbed → zemljana anoda
Groundbed is a buried item, such as junk steel or graphite rods, that serves as the anode for the cathodic protection of pipelines or other buried structures.
infrared spectroscopy → infracrvena spektroskopija
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is a technique used for determining the structure (and sometimes concentration) of molecules by observing how infrared radiation is absorbed by a sample.
deoxyribonucleic acid → dezoksiribonukleinska kiselina
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid with 2-deoxy-D-ribose as the sugar in its nucleotides. DNA contains encoded genetic information, specifically templates for the synthesis of all of an organism’s proteins and enzymes.
DNA was first identified in the 1869 by Swiss chemist Friedrich Miescher (1844-1895). In 1953, American biologist James Dewey Watson (1928-) and English physicist Francis Harry Compton Crick (1916–2004) had discovered that DNA occurs in the cell as a double helix, with two long strands of the molecule wound around each other, and further that the chemical structure of the molecule dictates that adenine (A) always aligns or pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) always pairs with guanine (G). It is this base pairing that allows DNA in a cell to copy itself, and transfer its information to a new cell. The diameter of the helix is 2.0 nm and there is a residue on each chain every 0.34 nm in the z direction. The angle between each residue on the same strand is 36°, so that the structure repeats after 10 residues (3.4 nm) on each strand.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Lewis structure." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table