Faraday’s laws of electrolysis → Faradayevi zakoni elektrolize
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are two laws found by British chemist and physicist Michael Faraday (1791-1867) in his experiments on electrolysis:
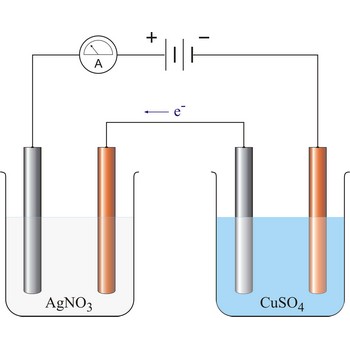
1. The quantity of matter extracted on the electrode is proportional to the quantity of charge (Q = I·t) which has flown in electrolysis time.
where z = number of electrons changed in reaction and F = Faraday’s constant which equals 96 487 C mol-1.
2. The masses of the elements liberated by the same quantity of electricity are directly proportional to their chemical equivalents.
96 487 C will discharge 1 mol Ag and 1/2 mol Cu. The relevant half reactions are:
Gibbs free energy → Gibbsova slobodna energija
Gibbs free energy (G) is an important function in chemical thermodynamics, defined by
where H is the enthalpy, S the entropy, and T the thermodynamic temperature. Gibbs free energy is the energy liberated or absorbed in a reversible process at constant pressure and constant temperature. Sometimes called Gibbs energy and, in older literature, simply free energy.
Changes in Gibbs free energy, ΔG, are useful in indicating the conditions under which a chemical reaction will occur. If ΔG is negative the reaction will proceed spontaneously to equilibrium. In equilibrium position ΔG = 0.
phase diagram → fazni dijagram
Phase diagram is a graphic representation of the equilibrium relationships between phases (such as vapour-liquid, liquid-solid) of a chemical compound, mixture of compounds, or solution.
The figure shows a typical phase diagram of an element or a simple compound. The stability of solid, liquid and gas phases depends on the temperature and the pressure. The three phases are in equilibrium at the triple point. The gas and liquid phases are separated by a phase transition only below the temperature of the critical point.
thermodynamic laws → termodinamički zakoni
Thermodynamic laws are the foundation of the science of thermodynamics:
First law: The internal energy of an isolated system is constant; if energy is supplied to the system in the form of heat dq and work dw, then the change in energy dU = dq + dw.
Second law: No process is possible in which the only result is the transfer of heat from a reservoir and its complete conversion to work.
Third law: The entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero as the thermodynamic temperature approaches zero.
distillation → destilacija
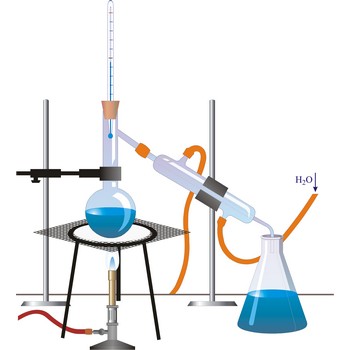
Distillation is a process of boiling a liquid and condensing and collecting the vapour. The liquid collected is the distillate. The usual purpose of distillation is purification or separation of the components of a mixture. This is possible because the composition of the vapour is usually different from that of liquid mixture from which it is obtained. Petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil are produced from petroleum by distillation.
absorbance → apsorbancija
Absorbance (A) is a logarithm of the ratio of incident radiant power (Po) to transmitted radiant power (P) through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls).
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
absorption → apsorpcija
Absorption is a phenomenon that occurs when matter crosses from one phase to another passing through the border surface and in the other phase more or less monotonously distributes itself in a concentration higher than the one within the first phase.
activity coefficient → koeficijent aktiviteta
Activity coefficient (γ or f) is a fractional number which, when multiplied by the molar concentration of a substance in solution, yields the chemical activity. This term gives an idea of how much interaction exists between molecules at higher concentration.
In solutions of very low ionic strength, when m is less than 0.01, the Debye-Hückel limiting law can be used to calculate approximate activity coefficients
where γi = activity coefficient of the species i, zi = charge on the species i and μ = ionic strength of the solution.
adsorption → adsorpcija
Adsorption is a process in which molecules of gas, of dissolved substances in liquids, or of liquids adheres in an extremely thin layer to surfaces of solid bodies with which they are in contact.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Gibbsov zakon faza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table