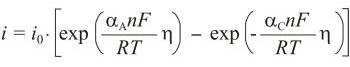coal → ugljen
Coal is a black or brownish-black, combustible sedimentary rock, with 30 % (lignite) to 98 % (anthracite) carbon by weight, mixed with various amounts of water and small amounts of sulfur and nitrogen compounds. It is formed from plant matter that decayed in swamps and bogs that has been compressed and altered by geological processes over millions of years. Coal is primarily used as a fuel.
computational chemistry → kompjutacijska kemija
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry concerned with the prediction or simulation of chemical properties, structures, or processes using numerical techniques.
concentration of ore → koncentriranje ruda
Concentration of ores is important industrial processes and is the first steps to the extraction of the metals. Normally, the ore is concentrated by separating it from the clay body in which it occurs either by gravity, sedimentation, or by a floatation process, before the extraction of the metal from the ore is started.
conduction → kondukcija
This process occurs most significantly in solids. The atoms or molecules in a solid state do not leave their mean positions, but continue to vibrate about their mean positions. They transfer heat energy from one atom to another. This happens because of the coupling between them due to mutually attractive forces.
crystallisation → kristalizacija
Crystallisation is process in which the melted substance from a saturated solution turns into solid substance (crystal).
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
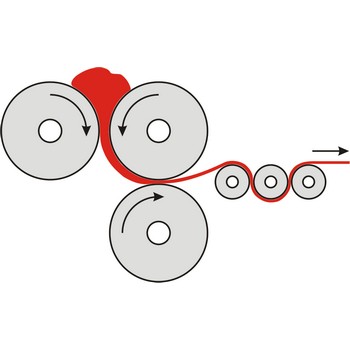
calendering → kalandriranje
Calendering is the process of forming materials to make a film/sheet by passing them through a series of hot rollers.
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
detection limits → granica detekcije
Detection limits is the smallest quantity of analyte which it is possible to determine by means of a given technique or procedure.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Born-Haberov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table