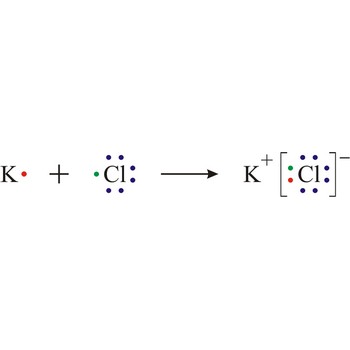hydration → hidratacija
Hydration is addition of water or the elements of water (i.e. H and OH) to a molecular entity. The term is also used in a more restricted sense for the process:
hydrosphere → hidrosfera
Hydrosphere (from the Greek for water sphere) is a discontinuous layer of water on, under, and over the Earth's surface. It includes all liquid and frozen surface waters, groundwater held in soil and rock, and atmospheric water vapour. Water continuously circulates between these reservoirs in what is called the hydrologic cycle, which is driven by energy from the Sun.
| Reservoir | V / 106 km3 | w / % |
|---|---|---|
| oceans | 1 370.0 | 97.25 |
| ice caps and glaciers | 29.0 | 2.05 |
| groundwater | 9.5 | 0.68 |
| lakes, rivers | 0.127 | 0.01 |
| soil moisture | 0.065 | 0.005 |
| atmosphere (as liquid equivalent of water vapour) | 0.013 | 0.001 |
| biosphere | 0.0006 | 0.00004 |
| TOTAL | 1 408.7 | 100 |
international system of units → međunarodni sustav jedinica
International System of Units (SI) is the unit system adopted by the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and recommended for use in all scientific and technical fields. It consists of seven base units (meter, kilogram, second, ampere, kelvin, mole, candela), plus derived units and prefixes.
ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
Joule-Thomson’s effect → Joule-Thomsonov efekt
Temperature of ideal gas will not be changed when it is repressed to a lower pressure, but when real gases are repressed to a lower pressure, a lower or higher temperature change appears under high pressures. The temperature change which appears at real gas expansion in a system into which energy is not brought is called Joule-Thomson’s effect. It was determined that when air is repressed by 1 bar, its temperature drops by 0.25 °C. That minute effect is completely irrelevant for most technical processes, but is also used in gas liquefying procedure.
kelvin → kelvin
Kelvin (K) is the SI base unit of thermodynamic temperature.
The kelvin, unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water. The unit was named after the British scientist Sir. W. Thompson, Lord Kelvin (1824-1907).kilogram → kilogram
Kilogram (kg) is the SI base unit of mass; it is equal to the mass of the international prototype of the kilogram.
The prototype of the standard is a cylinder of platinum-iridium alloy (90:10), 39 mm in diameter and 39 mm high. Prototype of the kilogram kept by the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (International Bureau of Weights and Measures) at Sèevres, near Paris.
lawrencium → lawrencij
Lawrencium was discovered by Albert Ghiorso, Torbjorn Sikkeland, Almon E. Larsh and Robert M. Latimer (USA) in 1961. Named in honour of Ernest O. Lawrence, inventor of the cyclotron. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Lawrencium was produced by bombarding a mixture of three isotopes of californium with boron-10 and boron-11 ions. Eight isotopes of lawrencium have been synthesized to date, with the longest-lived being lawrencium-256, which has a half-life of about 30 seconds.
lime → živo vapno
Lime (or quicklime) is the common name for calcium oxide (CaO). It is manufactured from limestone, CaCO3, by heating it to a high temperature (about 1 000 °C). At this temperature carbon dioxide, CO2, is released from the limestone creating calcium oxide, CaO.
A further process involves adding water in a process known as hydrating, which produces hydrated, or slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Born-Haberov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table