convection → konvekcija
Convection is the process by which heat is transferred from one part of a fluid to another by movement of the fluid itself. There are two methods by which this can be carried out.
Natural convection, in which movement occurs as a result of gravity. Heat transferred through a fluid medium, such as air or water, by currents that result from the rising of less dense, warm fluid and the sinking of heavier, cooler fluid.
Forced convection is where hot fluid is transferred from one region to another by a mechanical means (fans or pumps).
corrosion → korozija
Corrosion is a harmful and undesirable construction material consumption by the chemical activity of its surroundings. Corrosion concept refers to metal and nonmetal construction materials, but it is usually used for metals, Corrosion of metal, according to the mechanism process, is divided into chemical (corrosion in nonelectrolytes) and electrochemical (corrosion in electrolytes).
Chemical corrosion appears by direct action of molecule of some element or compound on metal, thus directly creating corrosion products.
Electrochemical corrosion of metals occurs in electrolytes, so reduction of metal atom into free cation appears which by secondary processes gives molecules of compound which are considered a corrosion product.
cracking → krekiranje
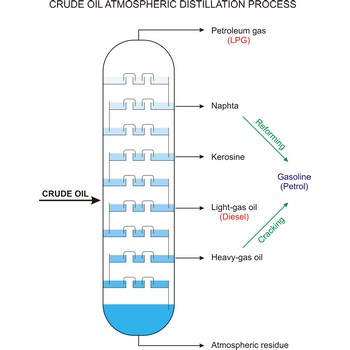
Cracking is the process whereby heavy molecules of petroleum or crude oil are broken down into hydrocarbons of lower molecular weight (especially in the oil-refining process).
crude oil → sirova nafta
Crude oil (petroleum) is a fossil fuel formed from plant and animal remains many million of years ago. It is occasionally found in springs or pools but is usually drilled from wells beneath the earth’s surface. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons with small quantities of other chemicals such as sulphur, nitrogen and oxygen. Crude is the raw material which is refined into petrol, heating oil, jet fuel, propane, petrochemicals, and other products.
nominal → nominalno
Nominal is used to describe a process where 100 % accuracy is not guaranteed. For example, sand filtres are usually sold to filtre to a nominal 10 μm, which means that they will filtre most particles of 10 μm and larger, but not all. A filtre which is guaranteed to filtre all particles of 10 μm would be termed absolute rather than nominal.
cryogenic fractionation → kriogena frakcinacija
Cryogenic fractionation is a process of separation of gases by cooling them until they enter their liquid state. Large scale gas production companies use this method to produce liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen etc. Gases have different boiling points (the temperature at which they change from liquid to gas). Oxygen has a boiling point of -183 °C, and nitrogen a boiling point of -195.8 °C. Therefore by cooling the gas mixture to -183 °C, the oxygen can be collected as liquid and the nitrogen remains its gaseous form.
Curie → Curie
Maria Sklodowska-Curie (1867-1934) Polish-born French chemist who went to Paris in 1891. She married the physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906) in 1985 and soon began work on seeking radioactive elements other than uranium in pitchblende (to account for its unexpectedly high radioactivity). By 1898 she had discovered radium and polonium although it took her years to purify them. In 1903 the Curies shared the Nobel Prize for physics with Henri Becquerel, who had discovered radioactivity.
decomposition → raspadanje
Decomposition occurs when chemical compounds are broken up into simple molecules, and even as far as their original elements. These processes are normally irreversible. An example of decomposition is when ammonium nitrate is heated. This produces nitrous oxide and water which are unable to recombine.
deionised water → deionizirana voda
Deionised water is water from which ionic salts have been removed by ion-exchange. It is used for many purposes as an alternative to distilled water.
| Type of water | Conductivity / µScm-1 |
|---|---|
| Ultrapure water | 0.05 |
| Distilled water | 0.5 |
| Tap water | 50 |
| Ocean water | 50 000 |
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Born-Haberov kružni proces." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table