magnesium → magnezij
Magnesium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word Magnesia, a district of Thessaly. It is lightweight, malleable, silvery-white metal. Burns in air with a brilliant white flame and reacts with water as temperature elevates. Can ignite in air. React violently with oxidants. Magnesium is found in large deposits in the form of magnesite, dolomite and other minerals. It is usually obtained by electrolysis of melted magnesium chloride (MgCl2) derived from brines, wells and sea water. Used in alloys to make airplanes, missiles and other uses for light metals. Have structural properties similar to aluminium.
nuclear reactor → nuklearni reaktor
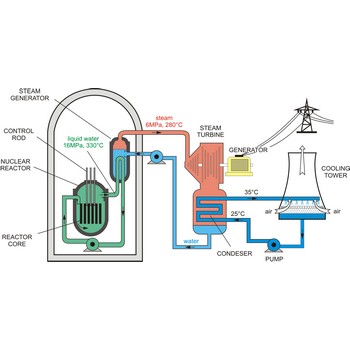
Nuclear reactor is an assembly of fissionable material (uranium-235 or plutonium-239) designed to produce a sustained and controllable chain reaction for the generation of electric power.
The essential components of a nuclear reactor are:
- The core, metal rods containing enough fissionable material to maintain a chain reaction at the necessary power level (as much as 50 t of uranium may be required).
- A source of neutrons to initiate the reaction (such as a mixture of polonium and beryllium)
- A moderator to reduce the energy of fast neutrons for more efficient fission (material such as graphite, beryllium, heavy water, and light water are used)
- A coolant to remove the fission-generated heat (water, sodium, helium, and nitrogen may be used)
- A control system such as rods of boron or cadmium that have high capture cross sections (to absorb neutrons)
- Adequate shielding, remote-control equipment, and appropriate instrumentation are essential for personnel safety and efficient operation.
salt fog test → ispitivanje u slanoj komori
Salt fog test is an accelerated corrosion test in which specimens are exposed to a fine mist of a solution usually containing sodium chloride (typically 5 %). Other contaminants can be added according to desired conditions. It is mainly used to determine the effectiveness of material finishes and protective coatings on materials. Salt-fog testing is also used to determine the effects of salt deposits on the electrical functions of electronic assemblies.
strontium → stroncij
Strontium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. Named after the village of Strontian in Scotland. It is soft, malleable, silvery-yellow metal. Combustible in air, will react with water. Exposed surfaces form protective oxide film. Metal ignites and burns readily. Strontium is found in minerals celestite and strontianite. Used in flares and fireworks for crimson colour. Strontium-90 is a long lived highly radioactive fallout product of atomic-bomb explosions.
tin → kositar
Tin has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word stannum meaning tin. It is silvery-white, soft, malleable and ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists oxygen and water. Dissolves in acids and bases. Organic tin compounds may be highly toxic. Tin is principally found in the ore cassiterite (SnO2) and stannine (Cu2FeSnS4). Used as a coating for steel cans since it is non-toxic and non-corrosive. Also in solder (33 %Sn:67 %Pb), bronze (20 %Sn:80 %Cu) and pewter. Stannous fluoride (SnF2), a compound of tin and fluorine is used in some toothpaste.
zinc → cink
Zinc was discovered by Andreas Marggraf (Germany) in 1746. The origin of the name comes from the German word zink. It is bluish-silver, ductile metal. Reacts with alkalis and acids. Tarnishes in air. Zinc is found in the minerals zinc blende (sphalerite) (ZnS), calamine, franklinite, smithsonite (ZnCO3), willemite and zincite (ZnO). Used to coat other metal (galvanizing) to protect them from rusting. Although some 90 % of the zinc is used for galvanizing steel. Zinc metal is used in the common dry-cell battery. Also used in alloys such as brass, bronze. Zinc compounds are also used in the manufacture of paints, cosmetics, plastics, electronic devices, and other products.
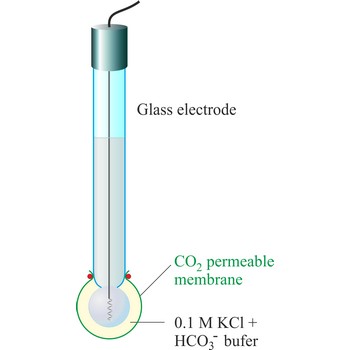
CO2 ion selective electrode → CO2 ion selektivna elektroda
The carbon dioxide ion selective electrode uses a gas-permeable membrane to separate the sample solution from the electrode internal solution. Dissolved carbon dioxide in the sample solution diffuses through the membrane until an equilibrium is reached between the partial pressure of CO2 in the sample solution and the CO2 in the internal filling solution. In any given sample the partial pressure of carbon dioxide will be proportional to the concentration of carbon dioxide. The diffusion across the membrane affects the level of hydrogen ions in the internal filling solution:
The hydrogen level of the internal filling solution is measured by the pH electrode located behind the membrane. The internal filling solution contains a high concentration of sodium bicarbonate (e.g. 0.1 mol/L NaHCO3) so that the bicarbonate level can be considered constant.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Zaštita žrtvovanom elektrodom." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table