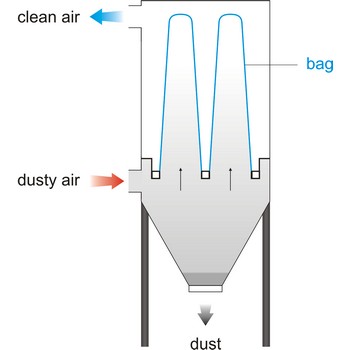
bag filter → vrećasti filtar
Bag filter is a unit within a mechanical system that bellows in a bag form when air flows through, cleaning the air by collecting particles of foreign matter. This system of filtering is rated the most efficient- in a range of 92 % to 95 %. Vacuum cleaner have a cloth filter bag.
Bag filter system is an economical method of liquid filtration consisting of the pressure vessel, restrainer basket and micron rated filter bag. Liquid flow is from the inside to the outside of the bag - dirt is trapped inside the bag.
filter paper → filtar papir
Filter paper is a quantitative paper used for filtering and made of pure cellulose treated with hydrochloric and hydrofluoric acid. This kind of paper burns out practically without any remains (less than 0.0001 g ashes). Different types of paper are marked with numbers; qualitative bears marking 595 or 597 and quantitative 589 or 590. Dependable upon precipitate character, different types of filter paper are used:
- black band (5891) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 20 s to 30 s. It is used for filtering of gelatinous precipitates.
- white band (5892) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 40 s to 60 s. It is used for coarse crystalline precipitates filtration.
- blue band (5893) - 100 mL of fluid flows through it in 200 s to 400 s. It is used for fine crystalline precipitates.
wrinkled filter paper → nabrani filtar-papir
Wrinkled filter paper is a filter made of wrinkled filter paper, by which, due to enlarged surface, fast filtering is achieved.
Buchner funnel → Buchnerov lijevak
Büchner funnel is one device used for pressure assisted filtration. Buchner funnel is a cylindrical porcelain filtering funnel (glass and plastic funnels are also available) that has a perforated plate on which the flat filter paper is placed. A vacuum in the flask underneath the filter allows atmospheric pressure on the sample to force the liquid through the filter paper. It is named after the German chemist Ernst Wilhelm Büchner (1850-1925) who designed this funnel in 1885.
clay triangle → trokut za žarenje
Clay triangle is a piece of laboratory equipment used in the process of heating substances by a Bunsen burner (e.g. to support a crucible when it’s being heated).
colloid → koloid
Colloids are systems in which there are two or more phases, with one (the dispersed phase) distributed in the other (the continuous phase). Moreover, at least one of the phases has small dimensions, in the range between 1 nm and 1 μm (10-9 m – 10-6 m). Dimension, rather than the nature of the material, is characteristic. In this size range, the surface area of the particle is large with respect to its volume so that unusual phenomena occur, e.g., the particles do not settle out of the suspension by gravity and are small enough to pass through filter membranes. Macromolecules (proteins and other high polymers) are at the lower limit of this range; the upper limit is usually taken to be the point at which the particles can be resolved in an optical microscope.
Colloidal particles may be gaseous, liquid, or solid, and occur in various types of suspensions:
Sols - dispersions of small solid particles in a liquid.
Emulsions - colloidal systems in which the dispersed and continuous phases are both liquids.
Gels - colloids in which both dispersed and continuous phases have a three-dimensional network throughout the material.
Aerosols - colloidal dispersions of liquid or solid particles in a gas.
Foams - dispersions of gases in liquids or solids.
filtration → filtriranje
Filtration is a procedure in which liquids are separated from the precipitate by passing a suspension through the filter. The precipitate remains on the filter and through it the filtrate passes. Gaseous heterogeneous mixtures can also be filtrated.
Hirsch funnel → Hirschov lijevak
Hirsch funnels are essentially smaller Büchner funnels and primarily used to collect a desired solid from a relatively small volume of liquid (1-10 mL). The main difference is that the plate is much smaller, while the walls of the funnel angle outward instead of being vertical. It is named after the German chemist Robert Hirsch (1856-1913).
nominal → nominalno
Nominal is used to describe a process where 100 % accuracy is not guaranteed. For example, sand filtres are usually sold to filtre to a nominal 10 μm, which means that they will filtre most particles of 10 μm and larger, but not all. A filtre which is guaranteed to filtre all particles of 10 μm would be termed absolute rather than nominal.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Vrećasti filtar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table