Celsius → Celzijev stupanj
Celsius (°C) is a common but non-SI unit of temperature, defined by assigning temperatures of 0 °C and 100 °C to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
atmosphere → atmosfera
1. Atmosphere is the column of air which is extending several hundred kilometers above the surface the Earth's surface. The density of this air decreases as you proceed up from the surface. The air in the atmosphere consists of 78 % nitrogen, 21 % oxygen, and 0.9 % argon. The remaining 0.1 % of the atmosphere consists of ozone, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, helium, and neon. The atmosphere is divided into different regions. The lowest two layers are the troposphere (the layer closest to the earth) and the stratosphere respectively. These two layers contain more than 99 % of the atmospheric molecules.
2. Standard atmosphere (atm) is an obsolete pressure and stress unit which should be discontinued. It is unit of pressure equal to the air pressure measured at mean sea level.
1 atm = 101 325 Pa
Technical atmosphere (at) is an obsolete MKpS pressure and sttress derived unit.
1 at = 98 066.5 Pa
1 atm = 1.033 227 453 at
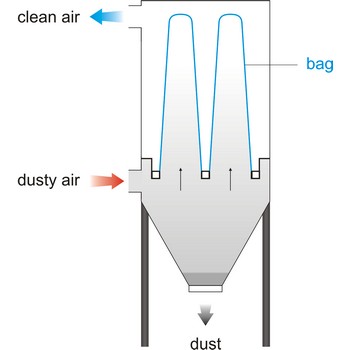
bag filter → vrećasti filtar
Bag filter is a unit within a mechanical system that bellows in a bag form when air flows through, cleaning the air by collecting particles of foreign matter. This system of filtering is rated the most efficient- in a range of 92 % to 95 %. Vacuum cleaner have a cloth filter bag.
Bag filter system is an economical method of liquid filtration consisting of the pressure vessel, restrainer basket and micron rated filter bag. Liquid flow is from the inside to the outside of the bag - dirt is trapped inside the bag.
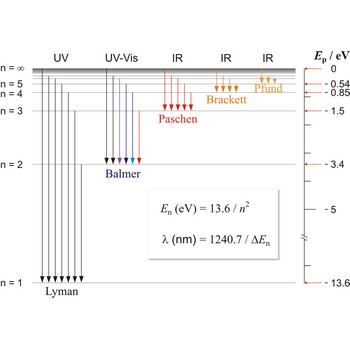
Balmer series → Balmerova serija
Balmer series, Balmer lines is a series of lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen that involve transitions to the n=2 state from states with n>2.
chemical property → kemijsko svojstvo
Chemical property is a property observed when a substance undergoes a transformation into one or more new substances. Measurement of a chemical property involves a chemical change. For example, determining the flammability of petrol involves burning it, producing carbon dioxide and water.
chlorination → kloriranje
1. Chlorination is an addition or substitution of chlorine in organic compounds.
2. Chlorination is a sterilisation of drinking and swimming pool water or oxidation of undesirable impurities, using chlorine or its compounds.
chlorosity → klorocitet
Chlorosity is the quantity determined by volumetric methods and is defined in the same manner as chlorinity except that the sample unit is 1 L of sea water rather than 1 kg of sea water weighed in vacuo.
barium → barij
Barium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy (England) in 1808. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word barys meaning heavy. It is soft, slightly malleable, silvery-white metal. Attacked by air and water. Soluble compounds toxic by ingestion. Barium is found in barytine (BaSO4) and witherite (BaCO3), never found in pure form due to its reactivity. Must be stored under kerosene to remain pure. Barite, or barium sulfate (BaSO4), when ground is used as a filter for rubber, plastics and resins. It is insoluble in water and so is used in X-rays of the digestive system. Barium nitrate, Ba(NO3)2, burns brilliant green and is used in fireworks.
base → baza
Historically, base is a substance that yields an OH - ion when it dissociates in solution, resulting in a pH>7. In the Brønsted definition, a base is a substance capable of accepting a proton in any type of reaction. The more general definition, due to G.N. Lewis, classifies any chemical species capable of donating an electron pair as a base. Typically, bases are metal oxides, hydroxides, or compounds (such as ammonia) that give hydroxide ions in aqueous solution.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table