tin → kositar
Tin has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word stannum meaning tin. It is silvery-white, soft, malleable and ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists oxygen and water. Dissolves in acids and bases. Organic tin compounds may be highly toxic. Tin is principally found in the ore cassiterite (SnO2) and stannine (Cu2FeSnS4). Used as a coating for steel cans since it is non-toxic and non-corrosive. Also in solder (33 %Sn:67 %Pb), bronze (20 %Sn:80 %Cu) and pewter. Stannous fluoride (SnF2), a compound of tin and fluorine is used in some toothpaste.
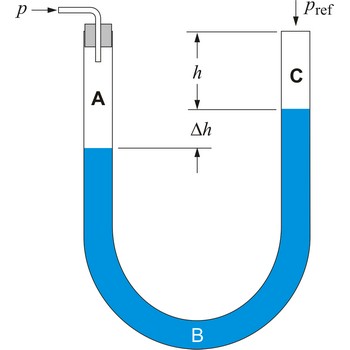
U-tube manometer → U-manometar
U-tube manometer contains water or mercury in a U-shaped tube, and is usually used to measure gas pressure. One end of the U tube is exposed to the unknown pressure field (P) and the other end is connected to a reference pressure source (usually atmospheric pressure) (Pref), shown in the schematic below.
If fluid C is the atmosphere, fluid B is the liquid in the U tube (e.g. water or mercury), and fluid A is a gas, then we can assume that ρB >> ρA, ρC. The pressure contributed by the weight of gas within the U tube can therefore be neglected. The gage pressure of the gas can be approximated by,
unsaturated fatty acid → nezasićena masna kiselina
Unsaturated fatty acid is a fatty acid whose carbon chain can absorb additional hydrogen atoms. Their carbon chain has one or more double or triple valence bond per molecule. The most important of these are:
| Oleic (9-octadecenoic acid) | CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH |
| Linoleic (9,12-octadecadienoic acid) | CH3(CHCH2)3(CH2CH=CH)2(CHCH2)7COOH |
| Linolenic (9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid) | CH3(CH2CH=CH)3(CHCH2)7COOH |
uranium → uranij
Uranium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. Named after the planet Uranus. It is silvery-white, dense, ductile, malleable, radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; tarnishes in air; attacked by steam and acids. Radiotoxic. Uranium occurs in many rocks, but in large amounts only in such minerals as pitchblende and carnotite. For many centuries it was used as a pigment for glass. Now it is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and in bombs.
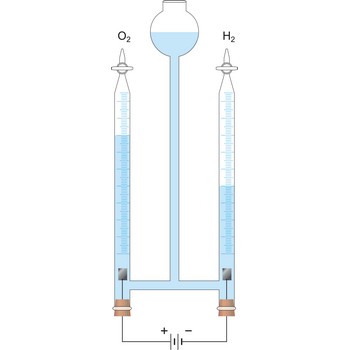
voltaic pile → Voltin stup
Voltaic pile was the first device that produced a continuous electric current. The first piles constructed by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta (1745-1827) in 1800 comprised alternating silver and zinc discs separated by cardboard soaked in brine. The pile can be stacked as high as you like, and each layer will increase the voltage by a fixed amount.
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
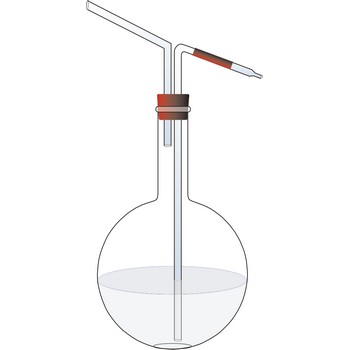
wash bottle → boca štrcaljka
Plastic wash bottle is a squeeze bottle made of low density polyethylene (LDPE) whose contents can be forced out through a narrow hole at the top by squeezing the bottle.
Glass wash bottle is a bottle fitted with two glass tubes pass through the cap, so that on blowing into one of the tubes a stream of water issuing from the other may be directed upon anything to be washed or rinsed, as a precipitate upon a filter.
Wilson’s chamber → Wilsonova komora
Wilson’s chamber is used for detection of radioactive radiation. Wilson’s chamber has a glass cylinder filled with air that has been saturated with water vapour. Radioactive radiation in its way ionises molecules of gas which then function as centres on which water vapour condenses into very small drops, thereupon showing Tyndall’s effect, i.e. is they are visible as a bright trail.
ytterbium → iterbij
Ytterbium was discovered by Jean de Marignac (France) in 1878. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, lustrous, malleable and ductile metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with water. Flammable dust. Ytterbium is found in minerals such as yttria, monazite, gadolinite and xenotime. Used in metallurgical and chemical experiments.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table