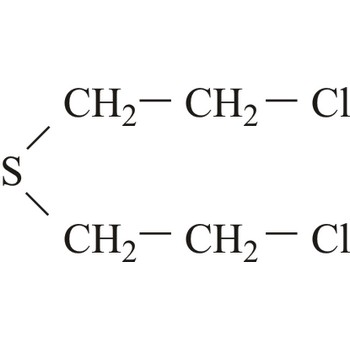living planet index → indeks života na planetu
The Living Planet Index (LPI) reflects changes in the health of the planet's ecosystems by tracking trends in nearly 8000 populations of vertebrate species. The LPI first calculates the annual rate of change for each species population in the dataset, then calculates the average change across all populations for each year from 1970, when data collection began, to 2007, the latest date for which data is available.
The Global LPI shows a decline of around 30 % from 1970 to 2007, based on 7953 populations of 2544 species of birds, mammals, amphibians, reptiles and fish.
luminescence → luminiscencija
Luminescence (from Latin lumen, light) is the emission of electromagnetic radiation (UV, visible or IR) from atoms or molecules as a result of the transition of an electronically excited state to a lower energy state, usually the ground state. Luminescence can be divided into categories by duration (fluorescence or phosphorescence) or by the mechanism that creates the light (radioluminescence, electroluminescence, photoluminescence, thermoluminescence, triboluminescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence). The prefix identifies the energy source responsible for generating or releasing the light.
Phosphorescence is emission of light from a substance exposed to radiation and persisting as an afterglow after the source of excitation has been removed. Fluorescence, on the other hand, is an almost instantaneous effect, ending within about 10-8 second after excitation.
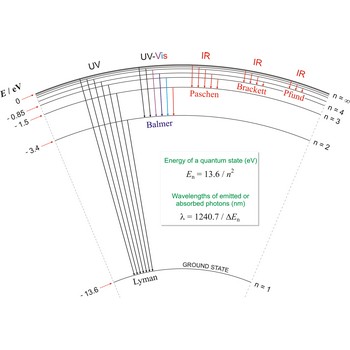
Lyman series → Lymanova serija
Lyman series is the series of lines in the spectrum of the hydrogen atom which corresponds to transitions between the ground state (principal quantum number n = 1) and successive excited states.
zeta potential → zeta potencijal
Zeta potential (ζ) is the potential across the interface of all solids and liquids. Specifically, the potential across the diffuse layer of ions surrounding a charged colloidal particle, which is largely responsible for colloidal stability. Also called electrokinetic potential.
mercury → živa
Mercury has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word hydrargyrum meaning liquid silver. It is heavy, silver-white metal, liquid at ordinary temperatures. Stable in air and water. Unreactive with alkalis and most acids. Gives off poisonous vapour. Chronic cumulative effects. Mercury only rarely occurs free in nature. The chief ore is cinnabar or mercury sulfide (HgS). Used in thermometers, barometers and batteries. Also used in electrical switches and mercury-vapour lighting products.
metal → metal
Metals are materials in which the highest occupied energy band (conduction band) is only partially filled with electrons.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity. The electrical conductivity of metals generally decreases with temperature.
- They are malleable and ductile in their solid state.
- They show metallic lustre.
- They are opaque.
- They have high density.
- They are solids (except mercury)
- They have a crystal structure in which each atom is surrounded by eight to twelve near neighbours
Their chemical properties generally are:
- They have one to four valence electrons.
- They have low ionisation potentials; they readily lose electrons.
- They are good reducing agents.
- They have hydroxides which are bases or amphoteric.
- They are electropositive.
Metallic characteristics of the elements decrease and non-metallic characteristics increase with the increase of valence electrons. Also metallic characteristics increase with the number of electron shells. Therefore, there is no sharp dividing line between the metals and non-metals.
Of the 114 elements now known, only 17 show primarily non-metallic characteristics, 7 others are metalloids, and 89 may be classed as metals.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
mustard agent → plikavac
Mustard agents are usually classified as blistering agents owing to the similarity of the wounds caused by these substances resembling burns and blisters. However, since mustard agents also cause severe damage to the eyes, respiratory system and internal organs, they should preferably be described as blistering and tissue-injuring agents. Normal mustard agent (yperite), 1,1-thio-bis-[2-chloroethane], reacts with a large number of biological molecules. The effect of mustard agent is delayed and the first symptoms do not occur between 2-24 hours after exposure. At room temperature, mustard agent is a liquid with low volatility and is very stable during storage.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Tekuće agregatno stanje." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table