hexagonal lattice → heksagonska rešetka
Hexagonal lattice has lattice points at the twelve corners of the hexagonal prism and at the centers of the two hexagonal faces of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=90° and γ=120°.
Kirchoff, Gustav → Kirchoff, Gustav
Gustav Kirchoff (1824-1887) was a German physicist who, with the chemist Robert Bunsen (1811-1899), laid the foundations of spectral analysis. He realized that the Fraunhofer lines in the Sun's spectrum were due to light from the photosphere being absorbed at those specific wavelengths by elements in the solar atmosphere. He also found that incandescent solids, liquids, and compressed gases emit a continuous spectrum. Use of the Bunsen burner in conjunction with a glass prism led to the development of the spectroscope in collaboration with the Bunsen and to the spectroscopic discovery of the elements rubidium (1860) and cesium (1861).
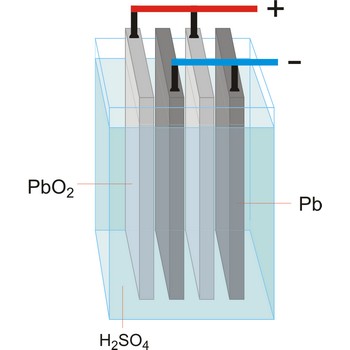
lead-acid battery → olovni akumulator
Lead-acid battery is a electrical storage device that uses a reversible chemical reaction to store energy. It was invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté. Lead-acid batteries are composed of a lead(IV) oxide cathode, a sponge metallic lead anode and a sulphuric acid solution electrolyte.
In charging, the electrical energy supplied to the battery is changed to chemical energy and stored. The chemical reaction during recharge is normally written:
In discharging, the chemical energy stored in the battery is changed to electrical energy. During discharge, lead sulfate (PbSO4) is formed on both the positive and negative plates. The chemical reaction during discharge is normally written:
Lead acid batteries are low cost, robust, tolerant to abuse, tried and tested. For higher power applications with intermittent loads however, they are generally too big and heavy and they suffer from a shorter cycle life.
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
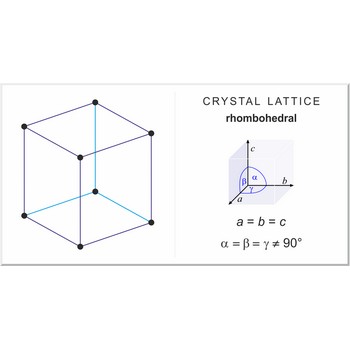
rhombohedral lattice → romboedarska rešetka
Rhombohedral (or trigonal) lattice has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a=b=c and interaxial angles α=β=γ≠90°.
rubidium → rubidij
Rubidium was discovered by Robert Bunsen and Gustav Kirchhoff (Germany) in 1861. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word rubidius meaning dark red or deepest red. It is soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Ignites in air. Reacts violently with water or oxidants. Rubidium occurs abundantly, but so widespread that production is limited. Usually obtained from lithium production. Used as a catalyst, photocells and vacuum and cathode-ray tubes.
selenium → selenij
Selenium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1817. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word selene meaning moon. It is soft metalloid similar to sulfur. Ranges from grey metallic to red glassy appearance. Unaffected by water. Soluble in alkalis and nitric acid. Burns in air. Toxic by inhalation or ingestion. Selenium is obtained from lead, copper and nickel refining. Conducts electricity when struck by light. Light causes it to conduct electricity more easily. It is used in photoelectric cells, TV cameras, xerography machines and as a semiconductor in solar batteries and rectifiers. Also colours glass red.
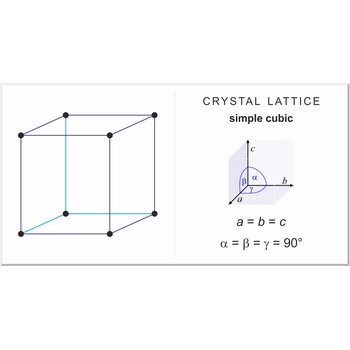
simple cubic lattice → jednostavna kubična rešetka
Simple or primitive cubic lattice (sc or cubic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a = b = c and interaxial angels α=β=γ=90°.
The simplest crystal structures are those in which there is only a single atom at each lattice point. In the sc structures the spheres fill 52 % of the volume. The number of atoms in a unit cell is one (8×1/8 = 1). This is only one metal (α-polonium) that have the sc lattice.
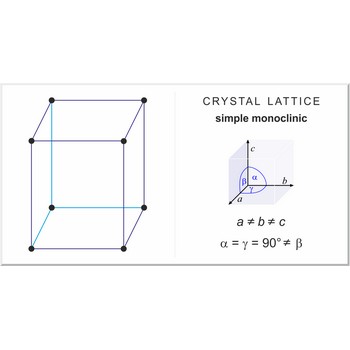
simple monoclinic lattice → jednostavna monoklinska rešetka
Simple or primitive monoclinic lattice (monoclinic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=γ=90°≠β.
simple orthorhombic lattice → jednostavna ortorompska rešetka
Simple or primitive orthorhombic lattice (orthorhombic-P) has one lattice point at the each corner of the unit cell. It has unit cell vectors a≠b≠c and interaxial angles α=β=γ=90°.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Sunčeva ćelija." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table