overpotential → prenapon
Overpotential (η) is a potential that must be applied in an electrolytic cell in addition to the theoretical potential required to liberate a given substance at an electrode. The value depends on the electrode material and on the current density.
positive pole → pozitivni pol
Positive pole is that half-cell in the electrochemical cell which has the most positive electrode potential.
reaction layer → reakcijski sloj
Reaction layer (in electrochemistry) is that layer of solution adjacent to an electrode within which a stationary distribution of electroactive species is established as the result of homogeneous reaction.
reversible cell → povrativi članak
Reversible cell is an electrical cell the chemical action in which can be reversed by passing through it a current opposite in direction to that generated by the cell.
thermal conductivity → toplinska vodljivost
Thermal conductivity (Λ) is rate of heat flow divided by the area and by the temperature gradient.
titrant → titrant
Titrant is the substance that quantitatively reacts with the analyte in a titration. The titrant is usually a standard solution added carefully to the analyte until the reaction is complete. The amount of analyte is calculated from the volume and concentration of titrant required for the complete reaction.
universal gas constant → univerzalna plinska konstanta
Universal gas constant R has the value of 8.314 472(15) J K-1 mol-1. It corresponds to the volume work performed by one mole of gas heated by 1 K at standard pressure.
electrogravimetry → electrogravimetrija
Electrogravimetry is an electroanalytical technique in which the substance to be determined (usually a metal) is deposited out on an electrode which is weighed before and after the experiment. The potential of the electrode must be carefully chosen to ensure that only the metal do be determined will deposit.
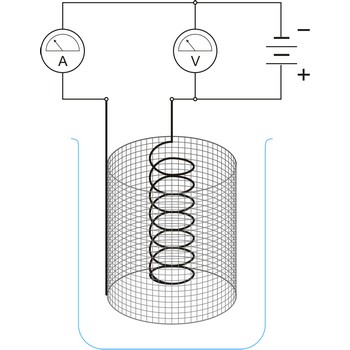
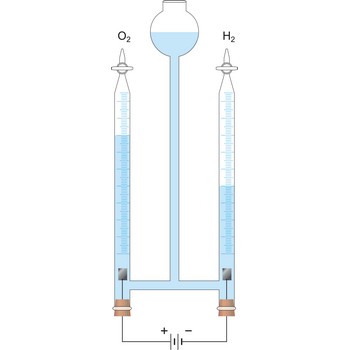
electrolysis → elektroliza
Electrolysis is the decomposition of a substance as a result of passing an electric current between two electrodes immersed in the sample.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Standardna vodikova elektroda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table