hydrogen → vodik
Hydrogen was discovered by Sir Henry Cavendish (England) in 1766. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words hydro and genes meaning water and generate. It is colourless, odourless gas, burns and forms explosive mixtures in air. Reacts violently with oxidants. Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. Commercial quantities of hydrogen are produced by reacting superheated steam with methane or carbon. In lab work from reaction of metals with acid solutions or electrolysis. Most hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia and in metal refining. Also used as fuel in rockets. Its two heavier isotopes (deuterium and tritium) used respectively for nuclear fusion.
hydrogen bond → vodikova veza
Hydrogen is a bond formed by a hydrogen atom to an electronegative atom, and is denoted by dashed lines H-X---H-B. A hydrogen atom covalently bound to an oxygen (electronegative atom) has a significant positive charge and can form a weak bond to another electronegative atom.
ion-product constant → ionski produkt vode
The ion-product constant. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C
salt fog test → ispitivanje u slanoj komori
Salt fog test is an accelerated corrosion test in which specimens are exposed to a fine mist of a solution usually containing sodium chloride (typically 5 %). Other contaminants can be added according to desired conditions. It is mainly used to determine the effectiveness of material finishes and protective coatings on materials. Salt-fog testing is also used to determine the effects of salt deposits on the electrical functions of electronic assemblies.
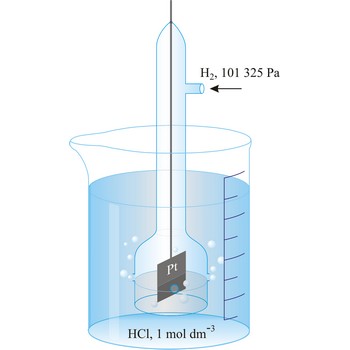
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
water gas → vodeni plin
Water gas (blue gas, synthesis gas) is a fuel gas used in industrial synthesis of organic chemicals, and in welding, glassmaking, and other high-temperature industrial applications. Water gas is made by passing steam over a bed of hot coal or coke. It mainly consists of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2), contaminated with small amounts of CO2, N2, CH4, and O2.
water hardness → tvrdoća vode
Hardness is defined as the concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions expressed in terms of calcium carbonate. These minerals in water can cause some everyday problems. They react with soap and produce a deposit called soap curd that remains on the skin and clothes and, because it is insoluble and sticky, cannot be removed by rinsing.
Hard water may also shorten the life of plumbing and water heaters. When water containing calcium carbonate is heated, a hard scale is formed that can plug pipes and coat heating elements. Scale is also a poor heat conductor. With increased deposits on the unit, heat is not transmitted to the water fast enough and overheating of the metal causes failure. Build-up of deposits will also reduce the efficiency of the heating unit, increasing the cost of fuel.
There are two types of water hardness, temporary and permanent.
Temporary Hardness is due to the bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, being present in the water. This type of hardness can be removed by boiling the water to expel the CO2, as indicated by the following equation:
Permanent hardness is due to calcium and magnesium nitrates, sulphates, and chlorides etc. This type of hardness cannot be eliminated by boiling.
| Water supply classification | |
|---|---|
| Hardness | Concentration of Calcium carbonate (mg/L) |
| Soft Water | 0 to 75 |
| Medium Hard Water | 75 to 150 |
| Hard Water | 150 to 300 |
| Very Hard Water | over 300 |
water ion product → ionski produkt vode
Water ion product (Kw) is a concentration product of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C, Kw = 1.0×10-14 mol2dm-6 = (Ka)(Kb)
water jet vacuum pump → vodena sisaljka
The water jet vacuum pump or vacuum aspirator is one of the most popular devices that produces vacuum in laboratories. The rapid flow of water through the device creates a vacuum in a side-arm that is connected to a vacuum application such a Buchner flask. The water jet vacuum pump creates a vacuum by means of Venturi effect named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Battista Venturi (1746–1822). The Venturi effect is the reduction in fluid pressure that results when a fluid flows through a constricted section of pipe. Water jet pumps are manufactured of glass, plastic or metal, depending on the conditions in which they are used.
chlorinity → klorinitet
Originally chlorinity (symbol Cl) was defined as the weight of chlorine in grams per kilogram of seawater after the bromides and iodides had been replaced by chlorides. To make the definition independent of atomic weights, chlorinity is now defined as 0.3285233 times the weight of silver equivalent to all the halides.
The Mohr-Knudsen titration method served oceanographers for more than 60 years to determine salinity from chlorinity. This modification of the Mohr method uses special volumetric glassware calibrated directly in chlorinity units. The Mohr method uses potassium chromate (K2CrO4) as an indicator in the titration of chloride ions chloride (plus a small amount of bromide and iodide) with a silver nitrate (AgNO3) standard solution.
The other halides present are similarly precipitated.
A problem in the Mohr titration was that silver nitrate is not well suited for a primary standard. The Danish physicist Martin Knudsen (1871-1949) suggested that a standard seawater (Eau de mer Normale or Copenhagen Normal Water) be created and distributed to oceanographic laboratories throughout the world. This water was then used to standardize the silver nitrate solutions. In this way all chlorinity determinations were referred to one and the same standard which gave great internal consistency.
The relationship between chlorinity Cl and salinity S as set forth in Knudsen's tables is
In 1962, however, a better expression for the relationship between total dissolved salts and chlorinity was found to be
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Slana voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table