water → voda
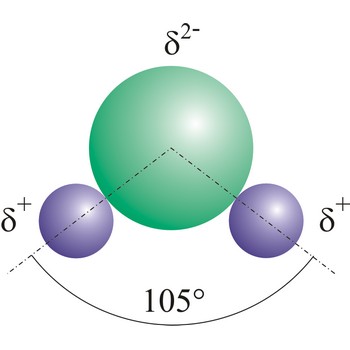
Water (H2O) (dihydrogen oxide) is a binary compound that occurs at room temperature as a clear colorless odorless tasteless liquid; freezes into ice below 0 °C and boils above 100 °C. Water is a chemical compound which is essential for living organisms and it is widely used as a solvent.
aqueous solution → vodena otopina
Aqueous solutions are those solutions where water is the solvent. An aqueous solution found in an equation describing a chemical reaction is denoted by the state symbol, (aq).
conductivity → vodljivost
Conductivity is a measure of the ability of a material to conduct electric current.
ionic conductor → ionski vodič
Ionic conductor is a material that conducts electricity with ions as charge carriers.
composition of ocean water → sastav oceanske vode
The proportions of the major constituents of ocean water are almost constant throughout the world. Salinity (total salt content) and the concentrations of individual chemical constituents in sea wateris given the units psu (practical salinity units). For most purposes one can assume that the new unit, psu, and the older unit, ‰, are synonymous.
The average composition of the ocean water is as shown on the following table.
| Constituent | Percentage of total salt |
|---|---|
| Chlorine | 55.3 % |
| Sodium | 30.8 % |
| Magnesium | 3.7 % |
| Sulphur | 2.6 % |
| Calcium | 1.2 % |
| Potassium | 1.1 % |
thermal conductivity → toplinska vodljivost
Thermal conductivity (Λ) is rate of heat flow divided by the area and by the temperature gradient.
water purification → pročišćavanje vode
Water purification is a procedure of harmful substances removal in order to obtain pure drinking-water.
water softener → omekšivač vode
Water softeners are substances which help remove constant water hardness. It reacts with calcium and magnesium salts, creating compounds that do not react with soap.
water softening → omekšavanje vode
Water softening is a process in which calcium and magnesium ions are removed from water. It is usually done by ion exchanger which exchanges removed ions with sodium ones.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Slana voda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table