Curie temperature → Curiejeva temperatura
For a ferromagnetic material, Curie temperature or Curie point (TC) is the critical temperature above which the material becomes paramagnetic. For iron the Curie point is 760 °C and for nickel 356 °C. It was named after the French physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906).
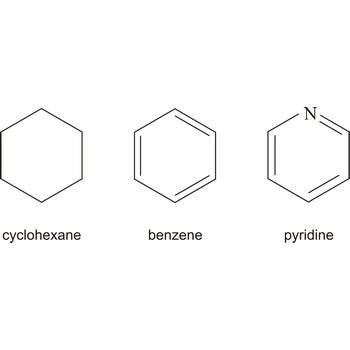
cyclic compound → ciklički spoj
Cyclic describing a compound that has a ring of atoms in its molecules. In homocyclic compounds all the atoms in the ring are of the same type, e.g. benzene (C6H6) and cyclohexane (C6H12). These two examples are also examples of carbocyclic compounds; i.e. the rings are made of carbon atoms. If different atoms occur in the ring, as in pyridine (C5H5N), the compound is said to be heterocyclic.
cyclic voltammetry → ciklička voltametrija
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical measuring technique used for the determination of the kinetics and mechanism of electrode reactions. The potential of the working electrode is controlled (typically with a potentiostat) and the current flowing through the electrode is measured. It is a linear-weep voltammetry with the scan continued in the reverse direction at the end of the first scan. This cycle can be repeated a number of times, and is used for corrosion studies.
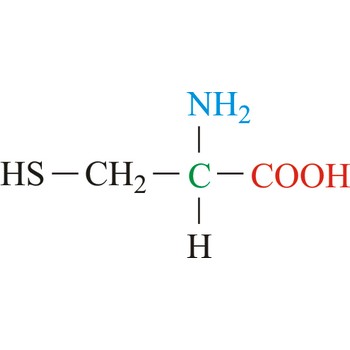
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
fogged metal → zamagljeni metal
Fogged metal is a metal whose lustre has been reduced because of a surface film, usually a corrosion product layer.
foreign matter → strana tvar
Foreign matter most commonly refers to the presence of unwanted or undesirable material present in foods or chemicals.
formaldehyde → formaldehid
Formaldehyde (methanal) is a colourless gas, HCHO; r.d. 0.815 (at -20 °C); m.p. -92 °C; b.p. -21 °C. It is the simplest aldehyde, made by the catalytic oxidation of methanol (500 °C; silver catalyst) by air. It forms two polymers: methanal trimer and polymethanal.
Dalton’s atomic theory → Daltonova atomska teorija
Dalton’s atomic theory is a theory of chemical combination, first stated by John Dalton in 1803. It involves the following postulates:
1. Elements consist of indivisible small particles (atoms).
2. All atoms of the same element are identical; different elements have different types of atom.
3. Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed.
4. ’Compound elements’ (i.e. compounds) are formed when atoms of different elements join in simple ratios to form ’compound atoms’ (i.e. molecules).
Dalton also proposed symbols for atoms of different elements (later replaced by the present notation using letters).
Dalton’s law → Daltonov zakon
Dalton’s law of partial pressure says that the total pressure eof gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of all gases partial pressures which make that mixture on the condition that they do not interact.
For example, if dry oxygen gas at 900 hPa is saturated with water vapor at 56 hPa, the pressure of the wet gas is 956 hPa.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "S.t.p.." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table