chlorophyll → klorofil
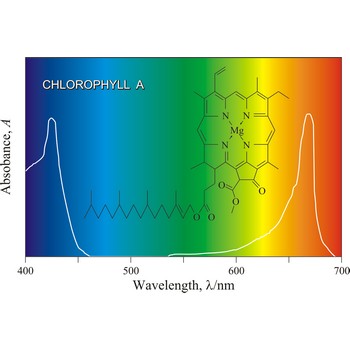
Chlorophyll is a green pigment present in green plants and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyll is essential in the transformation of light energy to chemical energy in photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light mostly in the blue and red ends of the visible spectrum, and very little in the green wavelengths. That green light is reflected, giving us the leaf colour we see.
chromatography → kromatografija
Chromatography is a method of separation of the components of a sample in which the components are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary while the other moves. In gas chromatography, the gas moves over a liquid or solid stationary phase. In liquid chromatography, the liquid mixture moves through another liquid, a solid, or a gel. The mechanism of separation of components may be adsorption, differential solubility, ion-exchange, permeation, or other mechanisms.
chromium → krom
Chromium was discovered by Louis-Nicholas Vauquelin (France) in 1797. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word chroma meaning colour. It is very hard, crystalline, steel-grey metal. The pure metal has a blue-white colour. It is hard, brittle and corrosion-resistant at normal temperatures. Hexavalent compounds toxic by skin contact. The most important chromium mineral is chromite [Fe,Mg(CrO4)]. Produced commercially by heating its ore in the presence of silicon or aluminium. Used to make stainless steel. It gives the colour to rubies and emeralds. Iron-nickel-chromium alloys in various percentages yield an incredible variety of the most important metals in modern technology.
Clapeyron equation → Clapeyronova jednadžba
Clapeyron equation (also called the Clausius-Clapeyron equation) is a relation between pressure and temperature of two phases of a pure substance that are in equilibrium,
where ΔtrsS is the difference in entropy between the phases and ΔtrsV the corresponding difference in volume.
ebullioscopic constant → ebulioskopska konstanta
Ebullioscopic constant (Eb) is the constant that expresses the amount by which the boiling point Tb of a solvent is raised by a nondissociating solute, through the relation
where b is the molality of the solute.
electroanalytical chemistry → elektroanalitička kemija
Electroanalytical chemistry chemistry is the application of electrochemical cells and electrochemical techniques for chemical analysis. The analyte is dissolved in the electrolyte of the cell, and one can perform either qualitative analysis (determination of the type of constituents present) or quantitative analysis (determination of the amount of a given constituent).
clay triangle → trokut za žarenje
Clay triangle is a piece of laboratory equipment used in the process of heating substances by a Bunsen burner (e.g. to support a crucible when it’s being heated).
cobalt → kobalt
Cobalt was discovered by Georg Brandt (Germany) in 1735. The origin of the name comes from the German word kobald meaning goblin or evil spirit. It is hard, ductile, lustrous bluish-grey metal. Surfaces stable in air. Reacts over time with dilute acids. It has remarkable magnetic properties. Cobalt occurs in compounds with arsenic and sulfur as in cobaltine (CoAsS) and linneite (Co3S4). Pure cobalt is obtained as a by-product of refining nickel, copper and iron. Used in many hard alloys; for magnets, ceramics and special glasses. Radioactive cobalt-60 is used in cancer therapy.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "S.t.p.." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table