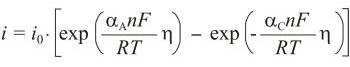Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation → Heyrovsky-Ilkovičeva jednadžba
The Heyrovsky-Ilkovic equation describes the entire current-potential curve (polarographic wave) of a reversible redox system in polarography
where R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature, F is the Faraday constant, n denotes the number of electrons taking part in the electrode reaction. E1/2 is a unique potential (for a given reaction and supporting electrolyte) termed the half-wave potential.
In order to obtain E1/2 from the above equation, we plot a graph of ln[(id-i)/i] against E. The intercept on the x-axis gives then an accurate value of E1/2. The slope of the obtained straight line is equal to nF/RT from which n is determined.
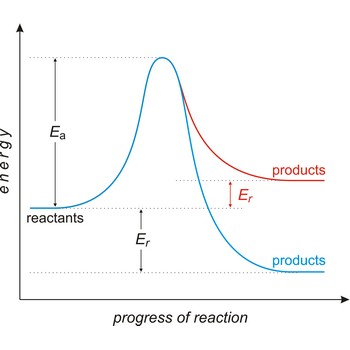
activation energy → energija aktivacije
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
amperometry → amperometrija
Amperometry is determining the concentration of a material in a sample by measuring electric current passing through a cell containing the solution.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
calomel electrode → kalomel elektroda
Calomel electrode is a type of half cell in which the electrode is mercury coated with calomel (Hg2Cl2) and the electrolyte is a solution of potassium chloride and saturated calomel. In the calomel half cell the overall reaction is
Table: Dependence of potential of calomel electrode upon temperature and concentration of KCl according to standard hydrogen electrode
| Potential vs. SHE / V | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| t / °C | 0.1 mol dm-3 | 3.5 mol dm-3 | sat. solution |
| 15 | 0.3362 | 0.254 | 0.2511 |
| 20 | 0.3359 | 0.252 | 0.2479 |
| 25 | 0.3356 | 0.250 | 0.2444 |
| 30 | 0.3351 | 0.248 | 0.2411 |
| 35 | 0.3344 | 0.246 | 0.2376 |
electromotive force → elektromotorna sila
Electromotive force (e.m.f. or EMF) is the difference in electric potential that exists between two dissimilar electrodes immersed in the same electrolyte or otherwise connected by ionic conductors.
electron volt → elektronvolt
Electron volt (eV) is a non-SI unit of energy used in atomic and nuclear physics, equal to approximately 1.602 177×10-19 J. The electron volt is defined as the kinetic energy acquired by an electron upon acceleration through a potential difference of 1 V.
cyclic voltammetry → ciklička voltametrija
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical measuring technique used for the determination of the kinetics and mechanism of electrode reactions. The potential of the working electrode is controlled (typically with a potentiostat) and the current flowing through the electrode is measured. It is a linear-weep voltammetry with the scan continued in the reverse direction at the end of the first scan. This cycle can be repeated a number of times, and is used for corrosion studies.
degree → stupanj
1. Degree is a unit of temperature on a specified scale. The temperatures of boiling and freezing water are: in the Fahrenheit system 212 and 32 degrees; in the Celsius system 100 and 0 (zero) degrees.
2. Degree is a unit of angular measure. A circle is divided into 360 degrees, represented by the symbol °. Degrees are each divided into 60 minutes. Each minute has 60 seconds. Symbols for degree, minute, and second for plane angle is placed after the numerical value and a no space between the numerical value and the unit symbol (α = 2°3'4").
3. In algebra, the degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. For example, 4x3 + 3x2 + x + 7 have degree 3.
electrical double layer → električni dvosloj
Electrical double layer is the structure of charge accumulation and charge separation that always occurs at the interface when an electrode is immersed into an electrolyte solution. The excess charge on the electrode surface is compensated by an accumulation of excess ions of the opposite charge in the solution. The amount of charge is a function of the electrode potential. This structure behaves essentially as a capacitor. There are several theoretical models that describe the structure of the double layer. The three most commonly used ones are the Helmholtz model, the Gouy-Chapman model, and the Gouy-Chapman-Stern model.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Redoks potencijal." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table