chain → lanac
Chain is a linear combination of the same type of atom in a molecule. In straight chain molecules, the atoms are arranged in a line, with each atom in the chain linked to one preceding atom and one succeeding atom of the same type. A closed chain molecule is a chain where the atoms are linked in a ring structure.
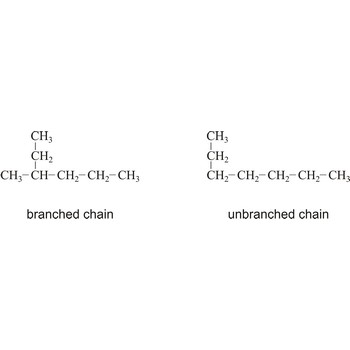
branched chain → razgranati lanac
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
lateral chain → postranični lanac
Lateral chain is a shorter chain of hydrocarbons which is connected to the main chain of hydrocarbon.
Boudouard’s equilibrium → Boudouardova ravnoteža
Boudouard’s equilibrium is established when carbon dioxide reacts with carbon. Because of reactions endothermity the temperature increase shifts the reaction rightwards and the temperature reduction leftwards.
chemical balance → kemijska ravnoteža
Chemical balance is a degree of reversible reaction in a closed system, when the forward and backward reaction happen at same rates and their effects annul each other, while the concentration of reactants and products stays the same.
dynamic equilibrium → dinamička ravnoteža
Dynamic equilibrium is established when two opposing processes are occurring at precisely the same rate, so that there is no apparent change in the system over long periods of time.
law of chemical equilibrium → zakon o kemijskoj ravnoteži
Law of chemical equilibrium (also called the law of mass action) states that the rate at which a substance reacts is proportional to its active mass (i.e. to its molar concentration). Thus, the velocity of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the concentration of the reactants.
thermodynamic equilibrium → termodinmička ravnoteža
Thermodynamic equilibrium is a system equilibrium in which energy that it gains from its surroundings is exactly balanced by the energy that it loses, no matter how much time is allowed to pass.
equilibrium constant → konstanta ravnoteže
The equilibrium constant (K) was originally introduced in 1863 by Norwegian chemists C.M. Guldberg and P. Waage using the law of mass action. For a reversible chemical reaction represented by the equation
chemical equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the back reaction, so that the concentrations of products and reactants reach steady-state values.
The equilibrium constant is the ratio of chemical activities of the species A, B, C, and D at equilibrium.
To a certain approximation, the activities can be replaced by concentrations.
For gas reactions, partial pressures are used rather than concentrations
The units of Kp and Kc depend on the numbers of molecules appearing in the stoichiometric equation (a, b, c, and d).
The value equilibrium constant depends on the temperature. If the forward reaction is exothermic, the equilibrium constant decreases as the temperature rises. The equilibrium constant shows the position of equilibrium. A low value of K indicates that [C] and [D] are small compared to [A] and [B]; i.e. that the back reaction predominates.
The equilibrium constant is related to ΔrG°, the standard Gibbs free energy change in the reaction, by
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ravni lanac." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table