polymorphic transition → polimorfni prijelaz
Polymorphic transition is a reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure. For examples, the transitions of quartz (SiO2) at 1 143 K to tridymite, and at 1 743 K to cristobalite.
primary alcohol → primarni alkohol
Primary alcohols are alcohols where the hydroxyl group is attached to a primary carbon atom. Thus, it has the general structure, RCH2OH, where R is a hydrogen atom or an alkyl group.
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
polymorphism → polimorfija
Polymorphism is the ability of a solid substance to crystallise into more than one different crystal structure. Different polymorphs have different arrangements of atoms within the unit cell, and this can have a profound effect on the properties of the final crystallised compound. The change that takes place between crystal structures of the same chemical compound is called polymorphic transformation.
The set of unique crystal structures a given compound may form are called polymorphs. Calcium carbonate is dimorphous (two forms), crystallizing as calcite or aragonite. Titanium dioxide is trimorphous; its three forms are brookite, anatase, and rutile. The prevailing crystal structure depends on both the temperature and the external pressure.
Iron is a metal with polymorphism structure. Each structure stable in the range of temperature, for example, when iron crystallizes at 1 538 °C it is bcc (δ-iron), at 1 394 °C the structure changes to fcc (γ-iron or austenite), and at 912 °C it again becomes bcc (α-iron or ferrite).
Polymorphism of an element is called allotropy.
recrystallisation → rekristalizacija
Recrystallisation is a formation of a new, strain free grain structure from the existing one in cold worked metal, usually accomplished by heating. The change from one crystal structure to another, as occurs on heating or cooling through a critical temperature.
polystyrene → polistiren
Polystyrene is a vinyl polymer. Structurally, it is a long hydrocarbon chain, with a phenyl group attached to every other carbon atom. Polystyrene is produced by free radical vinyl polymerization, from the monomer styrene. Polystyrene or Styrofoam is used in the construction industry as insulating material and for production of containers.
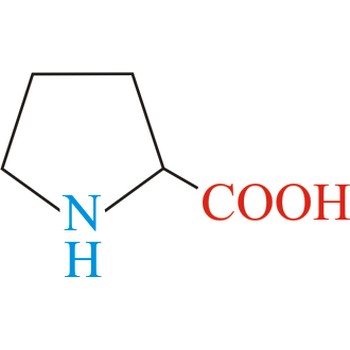
proline → prolin
Proline has an aliphatic side chain with a distinctive cyclic structure. It is unusual because it is conformationally restricted. The secondary amino (imino) group of proline residues is held in a rigid conformation that reduces the structural flexibility of polypeptide regions containing proline. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it.
- Abbreviations: Pro, P
- IUPAC name: pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H9NO2
- Molecular weight: 115.13 g/mol
resonance → rezonancija
Resonance is a stabilising quality of certain molecules that can be represented by considering the electron distribution in an ion or molecule as a composite of two or more forms, in those cases where a single form is an inadequate representation; for example, benzene and the carbonate ion. A various canonical structures can be drawn to show how electron delocalisation will explain the discrepancy, the difference in electron density
unit cell → jedinična ćelija
Unit cell is the smallest fragment of the structure of a solid that by repetition can generate the entire structure.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Prstenasta struktura." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table