polycondensational polymer → polikondenzacijski polimer
Polycondensational polymers are compounds which are obtained by condensation polymerization with successive repetitions of the condensation reaction.
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
condensational polymerisation → kondenzacijska polimerizacija
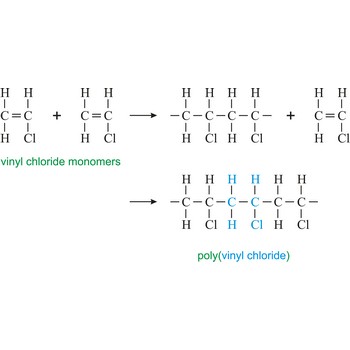
Condensational polymerisation is a reaction of polymerisation in which monomers together create a polymer by losing small molecules like water.
degree of polymerisation → stupanj polimerizacije
Degree of polymerisation is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or an oligomer molecule.
polymerization → polimerizacija
Polymerization is a reaction of connecting many monomers in one long molecule whereby polymers are created.
acrylic acid → akrilna kiselina
Acrylic acid (propenoic acid) is a colourless liquid, smelling like acetic acid. It can be formed by acrolein oxidation. It readily polymerizes and is used in the manufacture of acrylic resins, transparent plastic materials (organic glass).
copolymer → kopolimer
Copolymers are also known as heteropolymers. They are made from two (or more) different monomers, which usually undergo a condensation reaction with the elimination of a simple molecule, such as ammonia or water. A typical example is the condensation of 1,6-diaminohexane (hexamethylenediamine) with hexanedioic acid (adipic acid) to form nylon 6,6.
The properties of a polymeric plastic can most easily be modified if it is a copolymer of two or more different monomers, e.g. acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene copolymer (ABS). Varying the proportions of the component monomers can preselect its properties.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
epoxy resin → epoksi smola
Epoxy resins are thermosetting resins produced by copolymerising epoxide compounds with phenols (e.g. epichlorohydrin and bisphenol A). They contain ether linkages (-O-) and form a tight, cross-linked polymer network. Toughness, good adhesion, corrosive-chemical resistance, and good dielectric properties characterise epoxy resins. Most epoxy resins are two-part types which harden when blended.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Polimer." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table