tellurium → telurij
Tellurium was discovered by Franz Joseph Muller von Reichstein (Romania) in 1782. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word tellus meaning earth. It is silvery-white, brittle semi-metal. Unreactive with water or HCl; dissolves in HNO3; burns in air or oxygen. Tellurium is obtained as a by-product of copper and lead refining. Used to improve the machining quality of copper and stainless steel products and to colour glass and ceramics. Also in thermoelectric devices. Some is used in the rubber industry and it is a basic ingredient in manufacturing blasting caps.
terbium → terbij
Terbium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is soft, ductile, silvery-grey, rare earth metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with cold water. Terbium is found with other rare earths in monazite sand. Other sources are xenotime and euxenite, both of which are oxide mixtures that can contain up to 1 % terbium. It is used in modest amounts in special lasers and solid-state devices.
thorium → torij
Thorium was discovered by Jöns Jakob Berzelius (Sweden) in 1828. Named after Thor, the mythological Scandinavian god of war. It is heavy, grey, soft, malleable, ductile, radioactive metal. Tarnishes in air; reacts with water. Reacts violently with oxidants. Thorium is found in various minerals like monazite and thorite. Used in making strong alloys. Also in ultraviolet photoelectric cells. It is a common ingredient in high-quality lenses. Bombarded with neutrons make uranium-233, a nuclear fuel.
thulium → tulij
Thulium was discovered by Per Theodore Cleve (Sweden) in 1879. Named after Thule, an ancient name for Scandinavia. It is soft, malleable, ductile, silvery metal. Tarnishes in air. Reacts with water. Flammable dust. Thulium is found with other rare earths in the minerals gadolinite, euxenite, xenotime and monazite. Radioactive thulium is used to power portable X-ray machines, eliminating the need for electrical equipment.
tin → kositar
Tin has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word stannum meaning tin. It is silvery-white, soft, malleable and ductile metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Resists oxygen and water. Dissolves in acids and bases. Organic tin compounds may be highly toxic. Tin is principally found in the ore cassiterite (SnO2) and stannine (Cu2FeSnS4). Used as a coating for steel cans since it is non-toxic and non-corrosive. Also in solder (33 %Sn:67 %Pb), bronze (20 %Sn:80 %Cu) and pewter. Stannous fluoride (SnF2), a compound of tin and fluorine is used in some toothpaste.
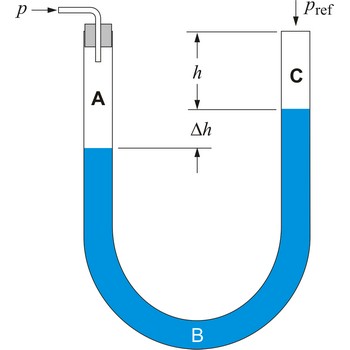
U-tube manometer → U-manometar
U-tube manometer contains water or mercury in a U-shaped tube, and is usually used to measure gas pressure. One end of the U tube is exposed to the unknown pressure field (P) and the other end is connected to a reference pressure source (usually atmospheric pressure) (Pref), shown in the schematic below.
If fluid C is the atmosphere, fluid B is the liquid in the U tube (e.g. water or mercury), and fluid A is a gas, then we can assume that ρB >> ρA, ρC. The pressure contributed by the weight of gas within the U tube can therefore be neglected. The gage pressure of the gas can be approximated by,
volumetric flask → odmjerna tikvica
Volumetric flasks are bottles made of glass, in a pear like in shape with long thin necks and flat bottoms. All come with a ground glass stopper for a tight seal. Volume marking is cut in glass with fluoride acid around the neck, so that parallax should be avoided (flask is put in front of the eyes so that one can see only a straight horizontal line). A volumetric flask is calibrated to contain (TC or In) the indicated volume of water at 20 °C when the bottom of the meniscus is adjusted to just rest on the center of the line marked on the neck of the flask. They are used for preparing the exactly known volume of sample solution and standard solutions of reagents. On each flask with volume designation a temperature on which the flask has been calibrated is designated.
volumetric pipette → prijenosna pipeta
Volumetric pipettes (transfer or belly pipette) are used in volumetric analysis, when there is a need for taking exact smaller volume of a sample solution or reagent. The upper tube of volumetric pipette has a ringlike marking (mark) which marks its calibrated volume. Pipettes calibrated to deliver (TD or Ex) the indicated volume. By sucking in (with mouth, propipette or a water pump) the liquid is pulled in a little bit above the mark and the opening of the pipet is closed with a forefingertip. Outer wall of pipet is wiped and, with a slight forefinger loosening, the liquid is released until it reaches the mark. Mark must figure as a tangent on a lower edge of the liquid meniscus. A pipette is emptied out by lifting the forefinger off and letting the liquid flow out of the pipette freely. After another 15 s and the tip of the pipette is pulled onto the inner wall of the vessel. It is absolutely forbidden to blow out the contents of the pipette.
wash bottle → boca štrcaljka
Plastic wash bottle is a squeeze bottle made of low density polyethylene (LDPE) whose contents can be forced out through a narrow hole at the top by squeezing the bottle.
Glass wash bottle is a bottle fitted with two glass tubes pass through the cap, so that on blowing into one of the tubes a stream of water issuing from the other may be directed upon anything to be washed or rinsed, as a precipitate upon a filter.
Wilson’s chamber → Wilsonova komora
Wilson’s chamber is used for detection of radioactive radiation. Wilson’s chamber has a glass cylinder filled with air that has been saturated with water vapour. Radioactive radiation in its way ionises molecules of gas which then function as centres on which water vapour condenses into very small drops, thereupon showing Tyndall’s effect, i.e. is they are visible as a bright trail.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Permanent hardness in water." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table