standard deviation → standardna devijacija
Standard deviation (σ) is a measure of the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. Standard deviation is a statistical term that measures the amount of variability or dispersion around an average
Suppose there are many measurements of a quantity presumed to be similar, like the size of peas in a pod. If the number of readings for each size were plotted, a bell-shaped curve would probably result, with a few small and large peas and most clustered around the average size. Around two-thirds of all measurements fall in the range spanned by the standard deviation, a measure of the spread.
standard hydrogen electrode → standardna vodikova elektroda
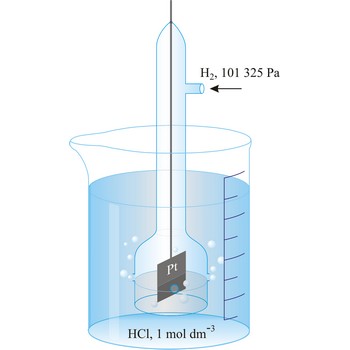
Standard hydrogen electrode is a system in which hydrogen ion and gaseous hydrogen are present in their standard states. The convention is to designate the cell so that the standard hydrogen electrode is written first.
The electrode is used as a reference (of zero) for the values of other standard electrode potentials.
starch → škrob
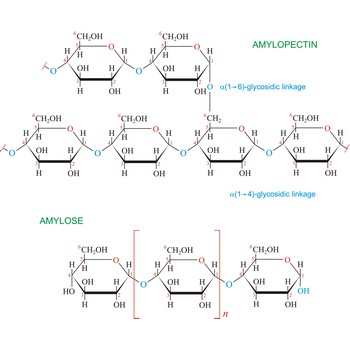
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
state of matter → agregatno stanje
State of matter is one of the tree physical states in which matter can exist, i.e. solid, liquid or gas. Plasma is sometimes regarded as the fourth state of matter. By means of heating a solid substance will cross to liquid state at its melting point. If we heat up a liquid and beyond, at its boiling point it will cross to gaseous state - vapour.
stereoisomer → stereoizomer
Stereoisomers are compounds that have identical chemical constitution, but differ as regards the arrangement of the atoms or groups in space. Stereoisomers fall into two broad classes: optical isomers (enantiomers) and geometric isomers (cis-trans).
stratosphere → stratosfera
Stratosphere is the part of the earth’s atmosphere extending from the top of the troposphere (typically 10 km to 15 km above the surface) to about 50 km. It is characterised by an increase in temperature with increasing altitude.
structural formula → strukturna formula
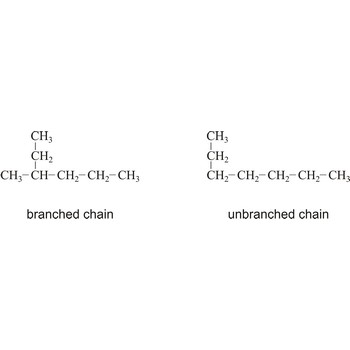
Structural formula is a two dimensional representations of the arrangement of the atoms in molecules. Atoms are represented by their element symbols and covalent bonds are represented by lines. The symbol for carbon is often not drawn.
styrene → stiren
Styrene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon (C6H5OC2H3O) colourless, toxic liquid with a strong aromatic aroma. It is soluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and carbon disulfide, but dissolves only slightly in water. It is used to make plastics such as polystyrene, ABS, styrene-butadiene rubber styrene-butadiene latex and unsaturated polyesters.
sucrose → saharoza
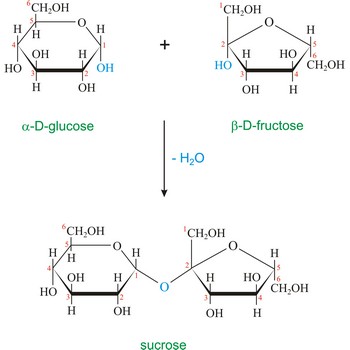
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Perioda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table