low-weight fractions → lake frakcije
Low-weight (petroleum) fractions have low boiling points and short carbohydrates chains.
fossil fuel → fosilno gorivo
Fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) are the fuels used by man as a source of energy. They are formed from the remains of living organisms and all have a high carbon or hydrogen content. They have value as fuels on the exothermic oxidation of carbon to form carbon dioxide
and the oxidation of hydrogen to form water
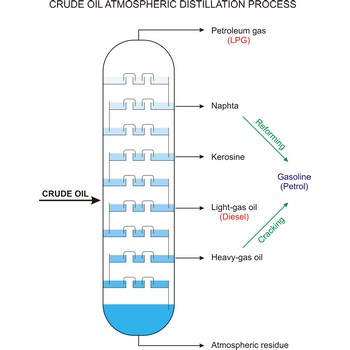
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
mineral oils → mineralna ulja
Mineral oils are oily liquids that are composed of hydrocarbons and are obtained as a product of petroleum, tar, coal, wood etc. distillation. They are used as lubricants.
non-soap cleanser → nesapunsko sredstvo za čišćenje
Non-soap cleansers (detergents) are synthetically produced from byproducts of oil refining and are used in the production of washing powder, shampoos and hair conditioners.
petrochemicals → petrokemikalije
Petrochemicals are the industrially important organic chemicals which are derived from petroleum or natural gas.
petroleum ether → petroleter
Petroleum ether is the petroleum fraction consisting of C5 and C6 hydrocarbons and boiling in the range 35 °C to 60 °C; commonly used as a laboratory solvent.
white spirit → bijeli špirit
White spirit (mineral spirits, petroleum spirits) is a paraffin-derived clear, transparent liquid which is a common organic solvent used in painting and decorating.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Nafta." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table