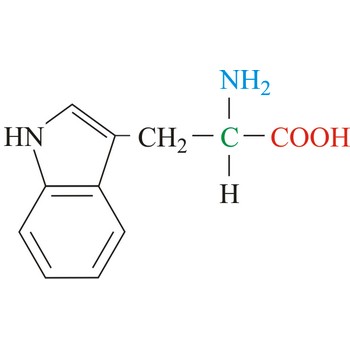
tryptophan → triptofan
Tryptophan is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tryptophan is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tryptophan has the largest side chain and is the least common amino acid in proteins. It has spectral properties that make it the best inherent probe for following protein folding and conformational changes associated with biochemical processes. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Trp, W
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C11H12N2O2
- Molecular weight: 204.23 g/mol
tungsten → volfram
Tungsten was discovered by Fausto and Juan Jose de Elhuyar (Spain) in 1783. Named after the tungsten mineral wolframite. It is hard, steel-grey to white metal. Highest melting point of all metals. Resists oxygen, acids and alkalis. Tungsten occurs in the minerals scheelite (CaWO4) and wolframite [(Fe,Mn)WO4]. Made into filaments for vacuum tubes and electric lights. Also as contact points in cars. Tungsten carbide is extremely hard and is used for making cutting tools and abrasives.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
uranium → uranij
Uranium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. Named after the planet Uranus. It is silvery-white, dense, ductile, malleable, radioactive metal. Resists alkalis; tarnishes in air; attacked by steam and acids. Radiotoxic. Uranium occurs in many rocks, but in large amounts only in such minerals as pitchblende and carnotite. For many centuries it was used as a pigment for glass. Now it is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors and in bombs.
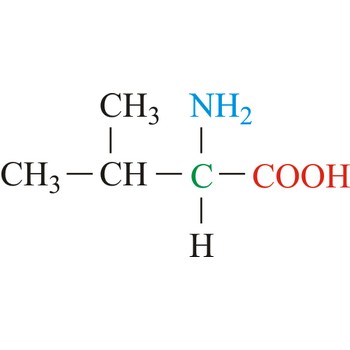
valine → valin
Valine is hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic side chain. It is a member of the branched-chain amino acid family, along with leucine and isoleucine. Valine differs from threonine by replacement of the hydroxyl group with a methyl substituent, but they are of roughly the same shape and volume. The nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tend to cluster together within proteins, stabilizing protein structure by means of hydrophobic interactions. Valine is an essential amino acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized in the body and must be obtained through dietary sources.
- Abbreviations: Val, V
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-methylbutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C5H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 117.15 g/mol
vanadium → vanadij
Vanadium was discovered by A. M. del Rio (Spain) in 1801 and rediscovered by Nils Sefstrom (Sweden) in 1830. Named after Vanadis, the goddess of beauty in Scandinavian mythology. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Resistant to corrosion by moisture, air and most acids and alkalis at room temperature. Exposed surfaces form oxide coating. Reacts with concentrated acids. Vanadium is found in the minerals patronite (VS4), vanadinite [Pb5(VO4)3Cl] and carnotite [K2(UO2)2(VO4)2·3H2O]. Pure metal produced by heating with C and Cl to produce VCl3 which is heated with Mg in Ar atmosphere. It is mixed with other metals to make very strong and durable alloys. Vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst, dye and fixer-fixer.
volumetric flask → odmjerna tikvica
Volumetric flasks are bottles made of glass, in a pear like in shape with long thin necks and flat bottoms. All come with a ground glass stopper for a tight seal. Volume marking is cut in glass with fluoride acid around the neck, so that parallax should be avoided (flask is put in front of the eyes so that one can see only a straight horizontal line). A volumetric flask is calibrated to contain (TC or In) the indicated volume of water at 20 °C when the bottom of the meniscus is adjusted to just rest on the center of the line marked on the neck of the flask. They are used for preparing the exactly known volume of sample solution and standard solutions of reagents. On each flask with volume designation a temperature on which the flask has been calibrated is designated.
ytterbium → iterbij
Ytterbium was discovered by Jean de Marignac (France) in 1878. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, lustrous, malleable and ductile metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with water. Flammable dust. Ytterbium is found in minerals such as yttria, monazite, gadolinite and xenotime. Used in metallurgical and chemical experiments.
zinc → cink
Zinc was discovered by Andreas Marggraf (Germany) in 1746. The origin of the name comes from the German word zink. It is bluish-silver, ductile metal. Reacts with alkalis and acids. Tarnishes in air. Zinc is found in the minerals zinc blende (sphalerite) (ZnS), calamine, franklinite, smithsonite (ZnCO3), willemite and zincite (ZnO). Used to coat other metal (galvanizing) to protect them from rusting. Although some 90 % of the zinc is used for galvanizing steel. Zinc metal is used in the common dry-cell battery. Also used in alloys such as brass, bronze. Zinc compounds are also used in the manufacture of paints, cosmetics, plastics, electronic devices, and other products.
zirconium → cirkonij
Zirconium was discovered by Martin Heinrich Klaproth (Germany) in 1789. The origin of the name comes from the Arabic word zargun meaning gold colour. It is grey-white, lustrous, corrosion-resistant metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide protective film. Zirconium is found in many minerals such as zircon and baddeleyite. Used in alloys such as zircaloy this is used in nuclear applications since it does not readily absorb neutrons. Also baddeleyite is used in lab crucibles. Used in high-performance pumps and valves. Clear zircon (ZrSiO4) is a popular gemstone.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Masna kiselina." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table