optically active matter → optički aktivna tvar
Optically active matter, by polarized light passing through it, turns the flat of polarized light leftwards or rightwards.
orbital → orbitala
Orbital is the area in space about an atom or molecule in which the probability of finding an electron is greatest.
The possible atomic orbitals correspond to subshells of the atom. Thus there is one s-orbital for each shell (orbital quantum number l = 0). There are three p-orbitals (corresponding to the three values of l) and five d-orbitals. The shapes of orbitals depend on the value of l.
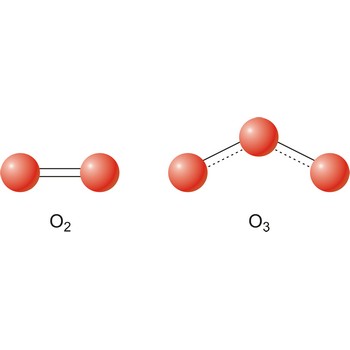
oxygen → kisik
Oxygen was discovered by Joseph Priestley (England) in 1774. The origin of the name comes from the Greek words oxy genes meaning acid and forming (acid former). It is colourless, odourless gas; pale blue liquid. Extremely reactive. Forms oxides with nearly all other elements except noble gases. It is the most abundant element in the earth’s crust and makes up almost 21 % of the atmosphere. Oxygen is obtained primarily from liquid air by fractional distillation. Small amounts are made in the laboratory by electrolysis of water. Used in steel making, welding and supporting life. Naturally occurring ozone (O3) in the upper atmosphere shields the earth from ultraviolet radiation.
paper chromatography → papirna kromatografija
Paper chromatography is one of the types of chromatography procedures which runs on a piece of specialized paper. It is a planar chromatography systems wherein a cellulose filter paper acts as a stationary phase on which separation of compounds occurs. The edge of the paper is immersed in a solvent, and the solvent moves up the paper by capillary action.
phenylalanine → fenilalanin
Phenylalanine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. It is quite hydrophobic and even the free amino acid is not very soluble in water. Phenylalanine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Phe, F
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO2
- Molecular weight: 165.19 g/mol
poison → otrov
Poisons are substance, which upon contact or being introduced into an organism, impair or prevent normal metabolic processes from taking place, thus altering the normal functioning of organs or tissues.
Poisons are molecules or material that tends to collect on a catalyst surface, blocking access to active sites or destroying their activities.
Poisons are substance that can reduce a nuclear reaction by absorbing neutrons, thereby preventing more fission. If enough poisons are present in a reactor core, the chain reaction will die out.
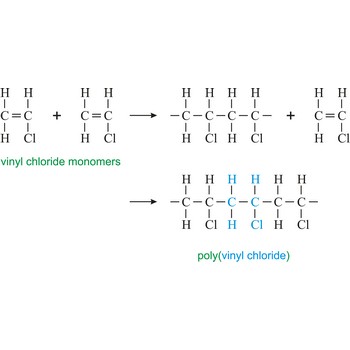
polymer → polimer
Polymer is a substance composed of molecules of high relative molecular mass (molecular weight), the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass (monomers). In most cases the number of monomers is quite large and is often not precisely known. A single molecule of a polymer is called a macromolecule. Polystyrene is light solid material obtained by polymerisation of styrene (vinyl benzene).
polymerization → polimerizacija
Polymerization is a reaction of connecting many monomers in one long molecule whereby polymers are created.
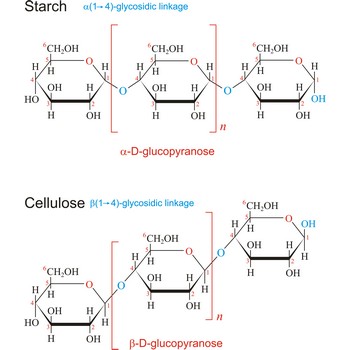
polysaccharide → polisaharid
Polysaccharides are compounds consisting of a large number of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked together by glycosidic bonds. When polysaccharides are composed of a single monosaccharide building block, they are termed homopolysaccharides. Heteropolysaccharides contain two or more different types of monosaccharide. Polysaccharides may have molecular weights of up to several million and are often highly branched. Since they have only the one free anomeric -OH group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show noticeable mutarotation. The most common polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kvadratna planarna geometrija molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table