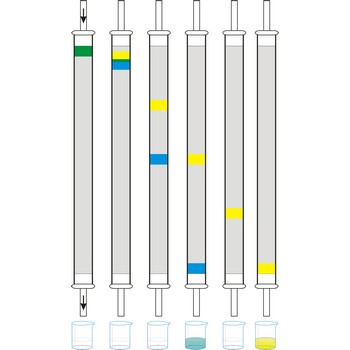
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
chromatography → kromatografija
Chromatography is a method of separation of the components of a sample in which the components are distributed between two phases, one of which is stationary while the other moves. In gas chromatography, the gas moves over a liquid or solid stationary phase. In liquid chromatography, the liquid mixture moves through another liquid, a solid, or a gel. The mechanism of separation of components may be adsorption, differential solubility, ion-exchange, permeation, or other mechanisms.
paper chromatography → papirna kromatografija
Paper chromatography is one of the types of chromatography procedures which runs on a piece of specialized paper. It is a planar chromatography systems wherein a cellulose filter paper acts as a stationary phase on which separation of compounds occurs. The edge of the paper is immersed in a solvent, and the solvent moves up the paper by capillary action.
supercritical fluid chromatography → superkritična fluidna kromatografija
Supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) is a hybrid of gas and liquid chromatography. SFC is of importance because it permits the separation and determination of a group of compounds that are not conveniently handled by either gas or liquid chromatography. These compounds are either nonvolatile or thermally labile so that gas chromatography cannot be used and they do not contain functional groups that make possible detection by liquid chromatography. SFC has been applied to a wide variety of materials including natural prodcuts, drugs, foods, pesticides and herbicides, fossil fuels, explosives and propellants.
thin layer chromatography → tankoslojna kromatografija
Thin layer chromatography. (TLC) is a technique for separating components in a mixture on the basis of their differing polarities. A spot of sample is placed on a flat sheet coated with silica and then carried along by a solvent that soaks the sheet. Different components will move different distances over the surface. TLC is a useful screening technique in clinical chemistry; for example, it can be used to detect the presence of drugs in urine.
carrier gas → plin nositelj
Carrier gas is the gas, (usually helium or nitrogen), which carries the sample undergoing analysis through the column in gas chromatography.
elution → eluacija
Elution is the process of removing an adsorbed material (adsorbate) from an adsorbent with a liquid (eluent). The solution consisting of the adsorbate dissolved in the eluent is the eluate. Elution is the process used to wash components of a mixture through a chromatography column.
fractional distillation → frakcijska destilacija
Fractional distillation is a procedure in which liquids of close boiling points are separated. It is conducted in fraction or rectification columns in a way that vapour phase created by distillation is condensed and the condensate thus obtained is redistilled. The procedure is repeated several times. Vapour phase always contains more volatile component than the liquid phase, at top of the column vapour of clean volatile component gets out and at the bottom of the column liquid of nonvolatile component.
Jones’s reductor → Jonesov reduktor
Jones’s reductor is a column filled with zinc amalgam. It is used for analyte reduction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kromatografija u koloni." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table