Lewis, Gilbert N. → Lewis, Gilbert N.
Gilbert Newton Lewis (1875-1946) is an American chemist whose theory of the electron pair fostered understanding of the covalent bond and extended the concept of acids and bases.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
cysteine → cistein
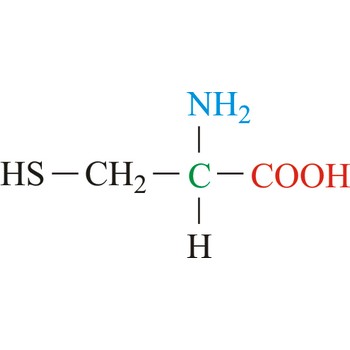
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
organometallic compound → organometalni spoj
Organometallic compounds are compounds in which there is a covalent connection between atoms of carbons and atoms of metal (C-Me).
Pauling scale → Paulingova skala
Pauling scale is a numerical scale of electronegativities based on bond-energy calculations for different elements joined by covalent bonds. Electronegativity is the power of an atom when in a molecule to attract eletrons to itself. Fluorine is the most electronegative element with a Pauling electronegativity value of 4.
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
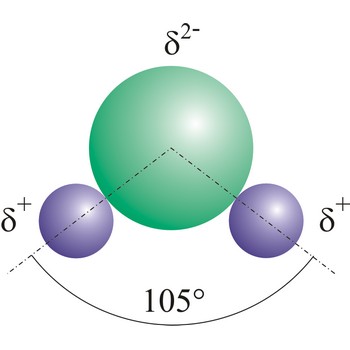
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
Fajans’ rules → Fajansova pravila
Fajans’ rules, formulated by American chemist of Polish origin. Kazimierz Fajans (1887-1975), indicating the extent to which an ionic bond has covalent character caused by polarisation of the ions. Covalent character is more likely if:
1. the charge of the ions is high;
2. the positive ion is small or the negative ion is large;
3. the positive ion has an outer electron configuration that is not a noble- gas configuration.
non-metal → nemetal
Non-metals are defined as elements that are not metals.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are poor conductors.
- They are brittle, not ductile in their solid state.
- They show no metallic lustre.
- They may be transparent or translucent.
- They have low density.
- They form molecules which consists of atoms covalently bonded; the noble gases are monoatomic.
Their chemical properties are generally:
- They usually have four to eight valence electrons.
- They have high electron affinities (except the noble gases)
- They are good oxidising agents (except the noble gases)
- They have hydroxides which are acidic (except the noble gases)
- They are electronegative.
resonance → rezonancija
Resonance is a stabilising quality of certain molecules that can be represented by considering the electron distribution in an ion or molecule as a composite of two or more forms, in those cases where a single form is an inadequate representation; for example, benzene and the carbonate ion. A various canonical structures can be drawn to show how electron delocalisation will explain the discrepancy, the difference in electron density
structural formula → strukturna formula
Structural formula is a two dimensional representations of the arrangement of the atoms in molecules. Atoms are represented by their element symbols and covalent bonds are represented by lines. The symbol for carbon is often not drawn.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kovalentna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table