nonpolar molecule → nepolarna molekula
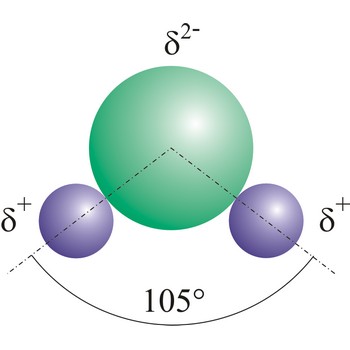
Nonpolar molecule is a molecule which has no separation of charge, so no positive or negative poles are formed. For example, the Cl2 molecule has no polar bonds (molecule with one type of atom), CH4 is a non-polar molecule (due to its symmetry). Nonpolar molecules do not dissolve in water as they cannot form hydrogen bonds (thus are hydrophobic) but do dissolve in lipids or fats (lipophilic).
polar molecule → polarna molekula
Polar molecules are molecules at which centres of gravity of positive and negative charge are not in the same point.
relative molecular mass → relativna molekularna masa
Relative molecular mass (Mr) is the ratio of the average mass per molecule or specified entity of a substance to 1/12 of the mass of nuclide 12C. Also called molecular weight. It is equal to the sum of the relative atomic masses of all the atoms that comprise a molecule. For example
Mr(H2SO4) = 2·Ar(H) + Ar(S) + 4·Ar(O)
= 2·1.0079 + 32.066 + 4·15.999
= 2.0158 + 32.066 + 63.996
= 98.078
stereospecific reaction → stereospecifična reakcija
Stereospecific reactions are reactions that proceed predominantly to a single stereoisomeric product out. All metabolic conversions involving chiral molecules are stereospecific.
optical activity → optička aktivnost
Optical activity is the ability of a chiral molecule to rotate the plane of plane-polairzed light. Molecules of an optically active substance cannot be superimposed on their own mirror images, just as your left hand cannot be superimposed on your right when both are held palm-down.
optically active matter → optički aktivna tvar
Optically active matter, by polarized light passing through it, turns the flat of polarized light leftwards or rightwards.
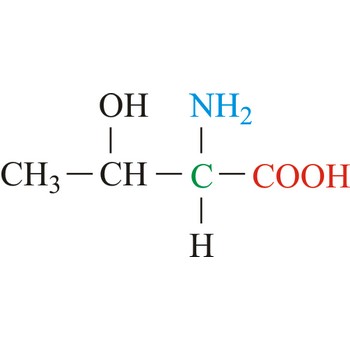
threonine → treonin
Threonine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. It differs from serine by having a methyl substituent in place of one of the hydrogens on the β carbon. Threonine is a site of phosphorylation and glycosylation which is important for enzyme regulation and cell signaling. It is an essential amino acid, which means that humans cannot synthesize it, so it must be ingested.
- Abbreviations: Thr, T
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-hydroxybutanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C4H9NO3
- Molecular weight: 119.12 g/mol
absorbance → apsorbancija
Absorbance (A) is a logarithm of the ratio of incident radiant power (Po) to transmitted radiant power (P) through a sample (excluding the effects on cell walls).
The absorption of light by a substance in a solution can be described mathematically by the Beer-Lambert law
where A is the absorbance at a given wavelength of light, ε is the molar absorbtivity or extinction coefficient (L mol-1 cm-1), unique to each molecule and varying with wavelength, b is the length of light path through the sample (cm), and c is the concentration of the compound in solution (mol L-1).
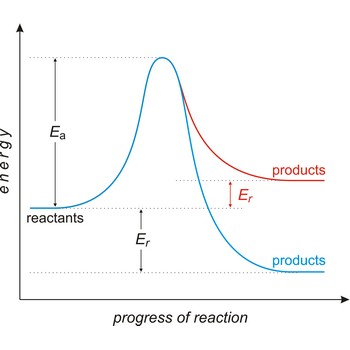
activation energy → energija aktivacije
Activation energy (Ea) is the energy that must be added to a system in order for a process to occur, even though the process may already be thermodynamically possible. In chemical kinetics, the activation energy is the height of the potential barrier separating the products and reactants. It determines the temperature dependence on the reaction rate.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Kiralne molekule." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table