electron → elektron
The electron is an elementary particle with a negative electric charge of (1.602 189 2±0.000 004 6)×10-19 C and a mass of 1/1837 that of a proton, equivalent to (9.109 534±0.000 047)×10-31 kg.
In 1897 the British physicist Joseph John (J.J.) Thomson (1856-1940) discovered the electron in a series of experiments designed to study the nature of electric discharge in a high-vacuum cathode-ray tube. Thomson interpreted the deflection of the rays by electrically charged plates and magnets as evidence of bodies much smaller than atoms that he calculated as having a very large value for the charge to mass ratio. Later he estimated the value of the charge itself.
Electrons are arranged in from one to seven shells around the nucleus; the maximum number of electrons in each shell is strictly limited by the laws of physics (2n2). The outer shells are not always filled: sodium has two electrons in the first shell (2×12 = 2), eight in the second (2×22 = 8), and only one in the third (2×32 = 18). A single electron in the outer shell may be attracted into an incomplete shell of another element, leaving the original atom with a net positive charge. Valence electrons are those that can be captured by or shared with another atom.
Electrons can be removed from the atoms by heat, light, electric energy, or bombardment with high-energy particles. Decaying radioactive nuclei spontaneously emit free electrons, called β particles.
europium → europij
Europium was discovered by Eugene Demarcay (France) in 1896. Named for the continent of Europe. It is soft, silvery-white metal. Extremely reactive with oxygen and water. Europium is obtained from monazite sand, which is a mixture of phosphates of calcium, thorium, cerium and most other rare earths. Used with yttrium oxide to make red phosphors for colour televisions.
gadolinium → gadolinij
Gadolinium was discovered by Jean de Marignac (France) in 1880. Named after the mineral gadolinite, named for J. Gadolin, a Finnish chemist and mineralogist. It is soft, ductile, silvery-white metal. Reacts slowly with water and oxygen. Dissolves in acids. Metal ignites and burns readily. Gadolinium is found with other rare earths in gadolinite and monazite sand. Used in steel alloying agents and the manufacture of electronic components.
terbium → terbij
Terbium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is soft, ductile, silvery-grey, rare earth metal. Oxidizes slowly in air. Reacts with cold water. Terbium is found with other rare earths in monazite sand. Other sources are xenotime and euxenite, both of which are oxide mixtures that can contain up to 1 % terbium. It is used in modest amounts in special lasers and solid-state devices.
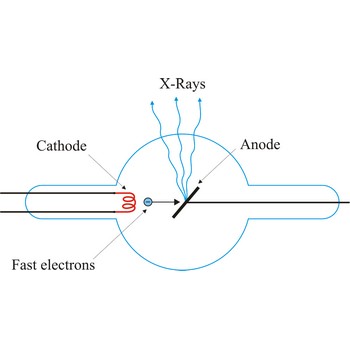
X-ray tube → rendgenska cijev
X-ray tube is a cathode ray tube that focuses energetic streams of electrons on a metal target, causing the metal to emit X-rays. The basic principle of the X-ray tube has not changed significantly since Roentgen's 1895 discovery. Current applied to a metal cathode (about 50 000 V) produces free electrons. The X-rays are produced when the rapidly moving electrons are suddenly stopped as they strike the metal target of the tube.
actinium → aktinij
Actinium was discovered by André Debierne (France) in 1899. The origin of the name comes from the Greek word aktinos meaning ray. It is heavy, silvery-white, very radioactive metal. Reacts with water. Glows in the dark. Actinium is extremely rare, found in all uranium ores. Usually obtained by treating radium with neutrons in a reactor.
activated charcoal → aktivni ugljen
Activated charcoal or activated carbon is charcoal that has been activated for adsorption by steaming or by heating in a vacuum. Charcoal is obtained by burning wood, nutshells, coconut husks or other materials. Charcoal becomes activated by heating it with steam to approximately 1000 °C in the absence of oxygen.
The chemical nature of amorphous carbon, combined with a high surface area makes it an ideal medium for the adsorption of organic chemicals. A single gram of such material can have 400 m2 to 1 200 m2 square meters of surface area. Activated charcoal is widely used to decolorize liquids, recover solvents, and remove toxins from water and air.
air stripping → zračni striping
Air stripping is a process for the removal of volatile organic contaminants from groundwater. The groundwater flows downward inside a tower filled with materials (the packing) over a large surface area. Air is introduced at the bottom of the tower and is forced upward past the falling water. The volatiles evaporate from the water and are collected in air filters or released to the atmosphere.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Katodna zraka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table