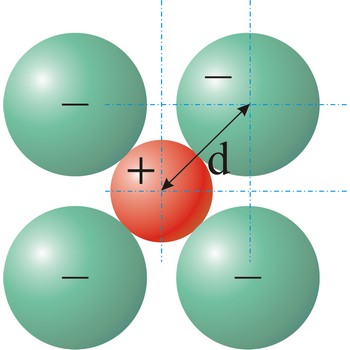
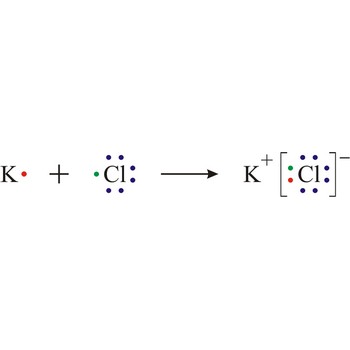ionic radius → ionski radijus
Ionic radius is the radius of anions and cations in crystalline ionic compounds, as determined by consistently partitioning the center-to-center distance of ions in those compounds. In general, negative ions have larger ionic radii than positive ions.
atom radius → radijus atoma
Atoms and molecules have no strict boundaries. The volume of a free atom is usually defined as that volume that contains 90 % of electron cloud. The radius of an atom represents half of interatom distance of two identical atoms which are in touch but are not interconnected either by a covalent or an ionic bond, but with a very weak van der Waals’s bond.
ionic conductor → ionski vodič
Ionic conductor is a material that conducts electricity with ions as charge carriers.
van der Waals’s radius → van der Waalsov radijus
Van der Waals’s radius is one half the distances between two nonbonded atoms, when attractive and repulsive forces between the atoms are balanced.
ion exchanger → ionski izmjenjivač
Ion-exchanger is a solid or liquid material containing ions that are exchangeable with other ions with a like charge that are present in a solution in which the material is insoluble. Ion-exchange resins consist of various copolymers having a cross-linked three-dimensional structure to which ionic groups have been attached.
ion-product constant → ionski produkt vode
The ion-product constant. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C
water ion product → ionski produkt vode
Water ion product (Kw) is a concentration product of hydrogen and hydroxide ions. For the reaction:
the equilibrium expression would be:
Note that all pure liquid terms are omitted, hence H2O does not appear in the denominator. At 25 °C, Kw = 1.0×10-14 mol2dm-6 = (Ka)(Kb)
complete ionic equation → potpuna ionska jednadžba
Complete ionic equation is a balanced equation that describes a reaction occurring in a solution, in which all strong electrolytes are written as dissociated ions.
ion exchange → ionska izmjena
Ion exchange is a process involving the adsorption of one or several ionic species accompanied by the simultaneous desorption (displacement) of one or more other ionic species.
ionic bond → ionska veza
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ionski radijus." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table