electron pair → elektronski par
Electron pair is two electrons within one orbital with opposite spins responsible for a chemical bond.
equivalent weight → ekvivalentna masa
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in a neutralization reaction is that mass of substance (molecule, ion, or paired ion) that either reacts with or supplies 1 mol of hydrogen ions in that reaction.
Equivalent weight of a substance participating in an oxidation/reduction reaction is that weight which directly or indirectly produces or consumes 1 mol of electrons.
conditional electrode potential → uvjetni elektrodni potencijal
Conditional or formal electrode potential (E°’) is equal to electrode potential (E) when overall concentrations of oxidised and reduced form in all its forms in a solution are equal to one. Conditional electrode potential includes all effects made by reactions that do not take part in the electron exchange, but lead to change of ion power, changes of pH, hydrolysis, complexing, precipitating, etc.
At 298 K (25 °C) and by converting natural (Napierian) logarithms into decimal (common, or Briggian) logarithms, Nernst’s equation for electrode potential can be written as follows:
conformation → konformacija
Conformation is one of the very large numbers of possible spatial arrangements of atoms that can be interconverted by rotation about a single bond in a molecule. The conformation of a molecule is not fixed, though one or another shape may be more likely to occur. There are two extreme cases:
Staggered conformation (antiperiplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as far apart as possible from the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
Eclipsed conformation (syn-periplanar) is a conformation about a carbon-carbon single bond in which the atoms on one carbon are as close as possible to the atoms on an adjacent carbon.
hydrophilic → hidrofilan
Hydrophilic is having a strong tendency to bind or absorb water, which results in swelling and formation of reversible gels. This property is characteristic of carbohydrates.
intermediate → intermedijer
Intermediate is a molecular or ionic species that is formed (directly or indirectly) from the reactants and reacts further (directly or indirectly) to form the products of the reaction. It does not accumulate during the course of the reaction.
cross-linking → umrežavanje
Cross-linking is an attachment of two chains of polymer molecules by bridges, composed of either an element, a group, or a compound, that join certain carbon atoms of the chains by primary chemical bonds, as indicated in the schematic diagram
Cross-linking occurs in nature in substances made up of polypeptide chains that are joined by the disulfide bonds of the cysteine residue, as in keratins or insulin. Cross-linking can be artificially effected, either adding a chemical substance (cross-linking agent), or by subjecting the polymer to high-energy radiation. Examples are: vulcanisation of rubber with sulphur, cross-linking of polystyrene with divinylbenzene, or cross-linking of polyethylene by means of high-energy radiation.
Cross-linking has the effect of changing a plastic from thermoplastic to thermosetting. Thus, it also increases strength, heat and electrical resistance, and especially resistance to solvents and other chemicals.
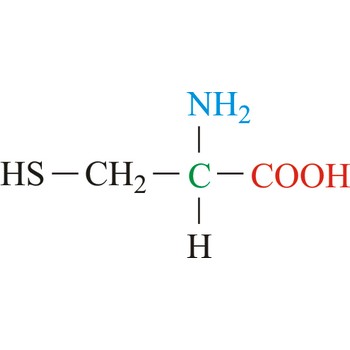
cysteine → cistein
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ionska veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table