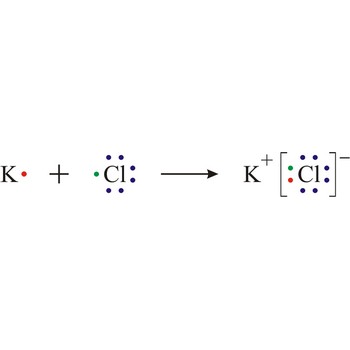ion selective electrode → ion selektivne elektrode
Ion selective electrode (ISE) is an electrode or electrode assembly with a potential that is dependent on the concentration of an ionic species in the test solution and is used for electroanalysis. Ion-selective electrodes are often membrane type electrodes.
Lewis structure → Lewisova struktura
Lewis structure is the representation of the electron arrangement in atoms, ions, or molecules by showing the valence electrons as dots placed around the symbols for the elements.
mass spectrometry → masena spectrometrija
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique in which ions are separated according to the mass/charge (m/e) ratio and detected by a suitable detector.
In a mass spectrometer a sample is ionised and the positive ions produced are accelerated into a high-vacuum region containing electric and magnetic fields. These fields deflect and focus the ions onto a detector. A mass spectrum is thus obtained, consisting of a series of peaks of variable intensity to which m/e values can be assigned. Different molecules can be identified by their characteristic pattern of lines.
metal → metal
Metals are materials in which the highest occupied energy band (conduction band) is only partially filled with electrons.
Their physical properties generally include:
- They are good conductors of heat and electricity. The electrical conductivity of metals generally decreases with temperature.
- They are malleable and ductile in their solid state.
- They show metallic lustre.
- They are opaque.
- They have high density.
- They are solids (except mercury)
- They have a crystal structure in which each atom is surrounded by eight to twelve near neighbours
Their chemical properties generally are:
- They have one to four valence electrons.
- They have low ionisation potentials; they readily lose electrons.
- They are good reducing agents.
- They have hydroxides which are bases or amphoteric.
- They are electropositive.
Metallic characteristics of the elements decrease and non-metallic characteristics increase with the increase of valence electrons. Also metallic characteristics increase with the number of electron shells. Therefore, there is no sharp dividing line between the metals and non-metals.
Of the 114 elements now known, only 17 show primarily non-metallic characteristics, 7 others are metalloids, and 89 may be classed as metals.
plasma → plazma
Plasma is a highly ionised gas in which the charge of the electrons is balanced by the charge of the positive ions, so that the system as a whole is electrically neutral. Plasmas are created by exposing gases at low pressure to an electric or electromagnetic field. In semiconductor processing, plasmas are used for etching and thin film deposition (the excited state of the gas makes it very reactive). In everyday life plasmas are used to give light in fluorescent light bulbs, neon lamps, and blue insect traps.
tyrosine → tirozin
Tyrosine is hydrophobic amino acids with aromatic side chain. Tyrosine is large aromatic residue that is normally found buried in the interior of a protein and is important for protein stability. Tyrosine has special properties since its hydroxyl side chain may function as a powerful nucleophile in an enzyme active site (when ionized) and is a common site for phosphorylation in cell signaling cascades. Tyrosine absorbs ultraviolet radiation and contributes to the absorbance spectra of proteins. It is not essential (or semi-essential) to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites.
- Abbreviations: Tyr, Y
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C9H11NO3
- Molecular weight: 181.19 g/mol
Wilson’s chamber → Wilsonova komora
Wilson’s chamber is used for detection of radioactive radiation. Wilson’s chamber has a glass cylinder filled with air that has been saturated with water vapour. Radioactive radiation in its way ionises molecules of gas which then function as centres on which water vapour condenses into very small drops, thereupon showing Tyndall’s effect, i.e. is they are visible as a bright trail.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ionic." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table