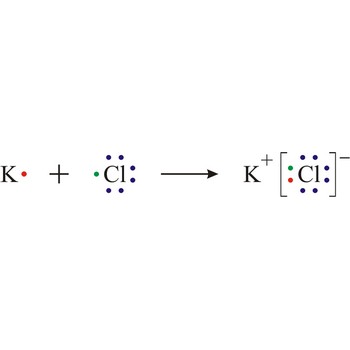complete ionic equation → potpuna ionska jednadžba
Complete ionic equation is a balanced equation that describes a reaction occurring in a solution, in which all strong electrolytes are written as dissociated ions.
ionic conductor → ionski vodič
Ionic conductor is a material that conducts electricity with ions as charge carriers.
ionic bond → ionska veza
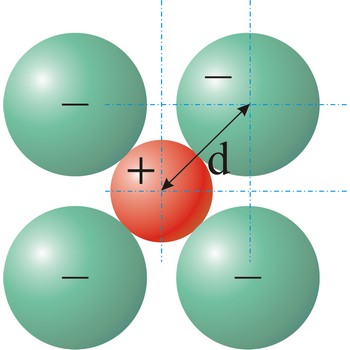
Ionic bond is a strong force of attraction holding atoms together in a molecule or crystal. Typically chemical bonds have energies of about 100 kJ mol-1. Ionic bond is a bond at which one of the participants, during the procedure of bonding, gives away its unpaired electrons to another atom so that both can achieve electron arrangement of the closest noble gas. In order to form an ionic bond one of the atoms must cross to the positively charged ion by losing certain number of electrons and the other atom must receive those electrons and cross to the negatively charged ion.
ionic radius → ionski radijus
Ionic radius is the radius of anions and cations in crystalline ionic compounds, as determined by consistently partitioning the center-to-center distance of ions in those compounds. In general, negative ions have larger ionic radii than positive ions.
ionic strength → ionska jakost otopine
Ionic strength (μ or I) is a measure of the total concentration of ions in a solution, defined by
where zi is the charge of ionic species i and ci is its concentration.
ionisation energy → energija ionizacije
Ionisation energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from an isolated atom or molecule (in its vibrational ground state) in the gaseous phase.
vertical ionisation energy → vertikalna energija ionizacije
Vertical ionisation energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom, molecule, or ion in the gas phase without moving any nuclei. The vertical ionisation energy is greater than or equal to the adiabatic ionisation energy.
ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
absorbed dose → apsorbirana doza
For any ionising radiation, absorbed dose (D) is the mean energy imparted to an element of irradiated matter divided by the mass of that element.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Ionic." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table