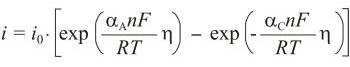standard electrode potential → standardni elektrodni potencijal
Standard electrode potential (E°) (standard reduction potentials) are defined by measuring the potential relative to a standard hydrogen electrode using 1 mol solution at 25 °C. The convention is to designate the cell so that the oxidised form is written first. For example,
The e.m.f. of this cell is -0.76 V and the standard electrode potential of the Zn2+|Zn half cell is -0.76 V.
potentiometric titration → potenciometrijska titracija
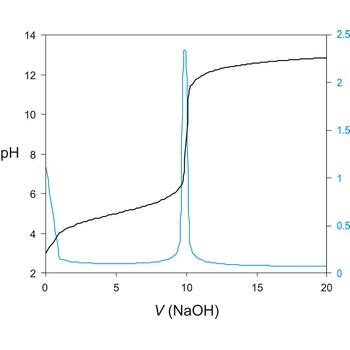
Potentiometric titration is a volumetric method in which the potential between two electrodes is measured (referent and indicator electrode) as a function of the added reagent volume. Types of potentiometric titrations for the determination of analytes in photoprocessing solutions include acid-base, redox, precipitation, and complexometric.
Potentiometric titrations are preferred to manual titrations, since they are more accurate and precise. They are also more easily adapted to automation, where automated titration systems can process larger volumes of samples with minimal analyst involvement.
A titration curve has a characteristic sigmoid curve. The part of the curve that has the maximum change marks the equivalence point of the titration. The first derivative, ΔE/ΔV, is the slope of the curve, and the endpoint occurs at the volume, V', where ΔE/ΔV has the maximum value.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
Butler-Volmer equation → Butler-Volmerova jednadžba
Butler-Volmer equation is an activation controlled reaction, the one for which the rate of reaction is controlled solely by the rate of the electrochemical charge transfer process, which is in turn an activation-controlled process. This gives rise to kinetics that are described by the Butler-Volmer equation:
where io is exchange current density, η is overpotential (η = E - Eo), n is number of electrons, αA is anodic transfer coefficient, and αC is cathodic transfer coefficient
carbon → ugljik
Carbon has been known since ancient times. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word carbo meaning charcoal. Graphite form of carbon is a black, odourless, slippery solid. Graphite sublimes at 3825 °C. Diamond form is a clear or colored; an extremely hard solid. C60 is Buckminsterfullerine. Carbon black burns readily with oxidants. Carbon is made by burning organic compounds with insufficient oxygen. There are close to ten million known carbon compounds, many thousands of which are vital to organic and life processes. Radiocarbon dating uses the carbon-14 isotope to date old objects.
cathode → katoda
Cathode is a negative electrode of an electrolytic cell to which positively charged ions (cations) migrate when a current is passed as in electroplating baths.
In a primary or secondary cell (battery or accumulator) the cathode is the electrode that spontaneously becomes negative during discharge, and form which therefore electrons emerge.
In vacuum electronic devices electrons are emitted by the cathode and flow to the anode.
cell potential → potencijal članka
Cell potential (E) is difference between anode and cathode potential. If the cell potential is positive, then the reaction is spontaneous.
cyclic voltammetry → ciklička voltametrija
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical measuring technique used for the determination of the kinetics and mechanism of electrode reactions. The potential of the working electrode is controlled (typically with a potentiostat) and the current flowing through the electrode is measured. It is a linear-weep voltammetry with the scan continued in the reverse direction at the end of the first scan. This cycle can be repeated a number of times, and is used for corrosion studies.
dialysis → dijaliza
Dialysis is a method by which large molecules (such as starch or protein) and small molecules (such as glucose or amino acids) may be separated in a solution by selective diffusion through a semipermeable membrane. Through this kind of membrane dissolved particles pass and colloid dimension particles fall behind. For example, if a mixed solution of starch and glucose is placed in a closed container made of a semipermeable substance (such as cellophane), which is then immersed in a beaker of water, the smaller glucose molecules will pass trough the membrane into the water, while the starch molecules remain behind.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Indikatorska elektroda." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table