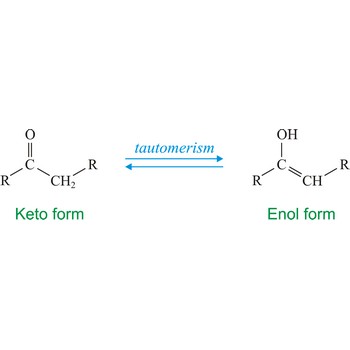
tautomerism → tautomerija
Tautomerism refers to equilibrium between two different structures of the same compound. Usually the tautomers differ in the point of attachment of a hydrogen atom. One of the most common examples of a tautomeric system is the equilibrium between a ketone (keto) and aldehyde (enol).
tear gas → suzavac
Tear gases is the common name for substances which, in low concentrations, cause pain in the eyes, flow of tears and difficulty in keeping the eyes open. Tear gases are used mainly in military exercises and in riot control, etc., but have also been used as a method of warfare. Irritating gases have been used in war since ancient times but it was not until after the Second World War that a more systematic search for effective substances was started. Among a long series of substances, three have become of greater importance than the others. These substances are chloroacetophenone (codename CN), orto-chlorobenzylidene-malononitrile (CS) and dibenz(b,f)-1,4-oxazepine (CR).
ununbium → ununbij
Ununbium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in February 1996. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as ununbium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Using the electromagnetic velocity filter SHIP, fusion-like residues of the reaction of 70Zn with enriched 208Pb targets were measured. Two chains of localized alpha-emitters were identified as originating with 277112 + 1n.
ununquadium → ununkvadij
The discovery of ununquadium was reported informally in January 1999 following experiments towards the end of December 1998 involving scientists at Dubna (Joint Institute for Nuclear Research) in Russia and the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, USA. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as ununquadium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. Only few atoms of element 114 (289114) has ever been made (through a nuclear reaction involving fusing a calcium atom with a plutonium atom) isolation of an observable quantity has never been achieved.
unununium → unununij
Unununium was discovered by S. Hofmann et al. collaboration at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory (Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung, GSI) in Darmstadt, Germany in December 1994. The new element has not yet been officially named, but it is known as unununium, according to the system designated by the IUPAC for naming new elements. It is synthetic radioactive metal. In bombardments of 209Bi targets with 64Ni using the velocity selector SHIP facility to discriminate in favor of the fused product, 272111 + 1n, three sets of localized alpha-decay chains were observed with position-sensitive detectors.
velocity → brzina
If a point-like object moves so that its position vector changes from being ri to rf, than the displacement Δr of object is
If a point-like object undergoes a displacement, Δr, in time Δt, its average velocity, v is defined as
The instantaneous velocity, v, is obtained from the average velocity by shrinking the time interval Δt towards zero. The average velocity approaches a limiting value, which is the velocity of a given instant:
Velocity is a vector quantity. If we plot the path of a moving particle as a curve in a coordinate system, the instantaneous velocity is always tangent to that curve.
SI unit for velocity is m s-1.
X-ray diffraction → rendgenska difrakcija
The regular array of atoms in a crystal is a three-dimensional diffraction grating for short-wavelength waves such as X-rays. The atoms are arranged in planes with interplanar spacing d. Diffraction maxima occur in the incident direction of the wave, measured from the surface of a plane of atoms, and the wavelength λ of the radiation satisfy Braggs’s law:
yttrium → itrij
Yttrium was discovered by Carl Gustaf Mosander (Sweden) in 1843. Named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden. It is silvery, ductile, fairly reactive metal. Exposed surfaces form oxide film. Easily combustible, reacts with oxygen in water to release hydrogen. Yttrium is found in minerals such as monazite, xenotime and yttria. Combined with europium to make red phosphors for colour TV’s. Yttrium oxide and iron oxide combine to form a crystal garnet used in radar.
zeolite → zeolit
Zeolite is a natural or synthetic hydrated aluminosilicate with an open three-dimensional crystal structure, in which water molecules are held in cavites in the latice. The water can be driven off by heating and the zeolite can then absorb other molecules of suitable size. Zeolites are used for separating mixtures by selective absorption.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Hexagonal_crystal_system." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table