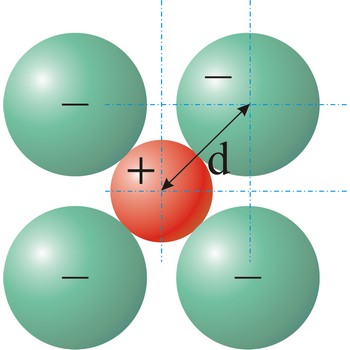
quasicrystal → kvazikristal
Quasicrystal is a solid having conventional crystalline properties but whose lattice does not display translational periodicity.
white light → bijela svjetlost
White light is a mixture of lights of all colours. If white light is passed through a glass prism or an optical lattice, it is separated into several colours (the visible light spectrum).
Bragg angle → Braggov kut
Bragg angle (Θ) is the angle between an incident X-ray beam and a set of crystal planes for which the secondary radiation displays maximum intensity as a result of constructive interference. British physicist Sir William Henry Bragg and his son Sir William Lawrence Bragg developed a simple relation for scattering angles, now call Bragg’s law.
which relates the angle θ between a crystal plane and the diffracted X-ray beam, the wavelength λ of the x-rays, the crystal plane spacing d, and the diffraction order n (any integer).
The diffraction experiment as presently considered is intended to provide quantitative information on the lattice constant and shape characteristics of the unit cell.
close-packed structure → gusta slagalina
Close packing is the packing of spheres so as to occupy the minimum amount of space. The name close packed refers to the packing efficiency of 74.05 %. There are two types of close packing: hexagonal and cubic. One layer, with atoms centered on sites labeled a. Two layers, with the atoms of the second layer centered on sites labeled b. The third layer can be placed on the sites labeled c (giving cubic close-packing) or over those marked a (giving hexagonal close-packing).
Curie temperature → Curiejeva temperatura
For a ferromagnetic material, Curie temperature or Curie point (TC) is the critical temperature above which the material becomes paramagnetic. For iron the Curie point is 760 °C and for nickel 356 °C. It was named after the French physicist Pierre Curie (1859-1906).
crystal system → kristalni sustav
Crystal system is a method of classifying crystalline substances on the basis of their unit cell. There are seven unique crystal systems. The simplest and most symmetric, the cubic (or isometric) system, has the symmetry of a cube. The other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic.
|
Crystal system
|
Unit-cell
|
Conditions on unit-cell edges and angles |
|
cubic |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ=90° |
|
hexagonal |
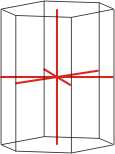 |
a≠c α=γ=90° β=120° |
|
tetragonal |
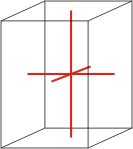 |
a=b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
rhombohedral |
 |
a=b=c α=β=γ≠90° |
|
orthorhombic |
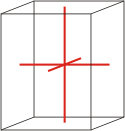 |
a≠b≠c α=β=γ=90° |
|
monoclinic |
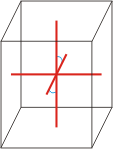 |
a≠b≠c α=γ=90°≠β |
|
triclinic |
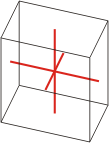 |
a≠b≠c α≠β≠γ≠90° |
glass electrode → staklena elektroda
Glass electrode is a hydrogen-ion responsive electrode usually consisting of a bulb, or other suitable form, of special glass attached to a stem of high resistance glass complete with internal reference electrode and internal filling solution system. Glass electrode is also available for the measurement of sodium ions.
The glass electrode, which consists of a thin wall glass bulb, has an extremely high electrical resistance. The membrane of a typical glass electrode (with a thickness of 0.03 mm to 0.1 mm) has an electrical resistance of 30 MΩ to 600 MΩ. The surface of a glass membrane must be hydrated before it will function as a pH electrode. When a glass surface is immersed in an aqueous solution then a thin solvated layer (gel layer) is formed on the glass surface in which the glass structure is softer. This applies to both the outside and inside of the glass membrane.
The simplest explanation for the working of the thin glass electrode is that the glass acts as a weak acid (Glass-H).
The hydrogen ion activity of the internal solution is held constant. When a solution of different pH from the inside comes in contact with the outside of the glass membrane, the glass is either deprotonated or protonated relative to the inside of the glass. The difference in pH between solutions inside and outside the thin glass membrane creates electromotive force in proportion to this difference in pH.
ionic radius → ionski radijus
Ionic radius is the radius of anions and cations in crystalline ionic compounds, as determined by consistently partitioning the center-to-center distance of ions in those compounds. In general, negative ions have larger ionic radii than positive ions.
ionisation → ionizacija
Ionisation is the process of producing ions. Certain molecules ionise in a solution; for example, acids ionise when dissolved in water.
Electron transfer also causes ionisation in certain reactions, for example sodium and chlorine react by transfer of a valence electron from the sodium atom to the chlorine atom to form the ions that constitute a sodium chloride crystal.
metallic glass → metalno staklo
Certain alloys can solidify by extremely rapid cooling out of melt without formation of a crystal lattice, that is in the amorphous form - such, amorphous alloys are so called metallic glasses. The alloy of zirconium, beryllium, titanium, copper, and nickel is one of the first metallic glasses that can be made in bulk and formed into strong, hard, useful objects.
Unlike pure metals and most metal alloys, metallic glasses have no regular crystalline structure. This lack of long range order or microstructure is related to such desirable features as strength and low damping which is one reason why the premier use for zirconium-based metallic glass is in the manufacture of expensive golf club heads. Metallic glasses can be quite strong yet highly elastic, and they can also be quite tough (resistant to fracture). Even more interesting are the thermal properties; for instance, just like an oxide glass, there is a temperature (called the glass transition temperature) above which a metallic glass becomes quite soft and flows easily. This means that there are lots of opportunities for easily forming metallic glasses into complex shapes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Heksagonska rešetka." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table