bidentate ligand → bidentatni ligand
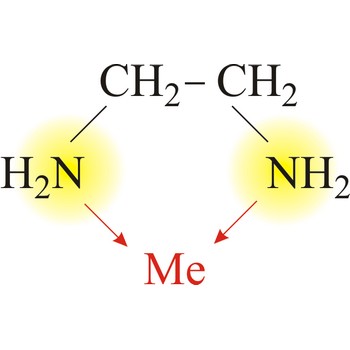
Bidentate ligand is a ligand that has two "teeth" or atoms that coordinate directly to the central atom in a complex. An example of a bidentate ligand is ethylenediamine. A single molecule of ethylenediamine can form two bonds to a metal ion. The bonds form between the metal ion and the nitrogen atoms of ethylenediamine.
electron pair → elektronski par
Electron pair is two electrons within one orbital with opposite spins responsible for a chemical bond.
hydrophilic → hidrofilan
Hydrophilic is having a strong tendency to bind or absorb water, which results in swelling and formation of reversible gels. This property is characteristic of carbohydrates.
borane → borani
Borane is any of the group of compounds of boron and hydrogen (B2H6, B4H10, B5H9, B5H11...), many of which can be prepared by action of acid on magnesium boride (Mg3B2). Boranes are a remarkable group of compounds in that their structures cannot be described using the conventional two-electron covalent bond model.
branched chain → razgranati lanac
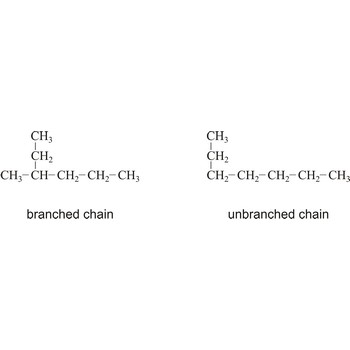
Branched chain is an open chain of atoms with one or more side chains attached to it.
Lewis acid → Lewisova kiselina
Lewis acid is an agent capable of accepting a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Lewis base → Lewisova baza
Lewis base is an agent capable of donating a pair of electrons to form a coordinate bond.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Glikozidna veza." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table