fructose → fruktoza
Fructose (fruit sugar) is a ketohexose (a six-carbon ketonic sugar), which occurs in sweet fruits and honey. Glucose and fructose have the same molecular formula, C6H12O6, but have different structures. Pure, dry fructose is a very sweet, white, odorless, crystalline solid. Fructose is one of the sweetest of all sugars and is combined with glucose to make sucrose, or common table sugar. An older common name for fructose is levulose, after its levorotatory property of rotating plane polarized light to the left (in contrast to glucose which is dextrorotatory). The polysaccharide inulin is a polymer of fructose.
glycogen → glikogen
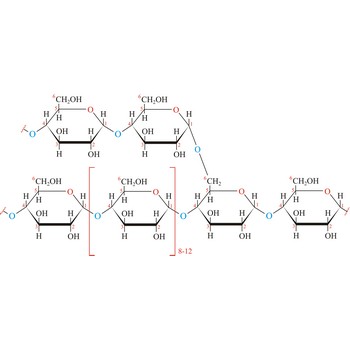
Glycogen (animal starch) is a polysaccharide that serves the same energy storage function in animals that starch serves in plants. Dietary carbohydrates not needed for immediate energy are converted by the body to glycogen for long term storage (principally in muscle and liver cells). Like amylopectin found in starch, glycogen is a polymer of α(1→4)-linked subunits of glucose, with α(1→6)-linked branches. Glycogen molecules are larger than those of amylopectin (up to 100 000 glucose units) and contain even more branches. Branch points occur about every 10 residues in glycogen and about every 25 residues in amylopectin. The branching also creates lots of ends for enzyme attack and provides for rapid release of glucose when it is needed.
lactose → laktoza
Lactose (milk sugar) is a disaccharide comprising one glucose molecule linked to a galactose molecule by an β(1→4)-glycosidic linkage. Lactose has a beta acetal. Lactose is manufactured by the mammary gland and occurs only in milk (from 4 % to 7 %). Lactose intolerance is a common medical condition that results in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and flatulence and is caused by reduced or absent activity of enzyme lactase.
Like cellobiose and maltose, lactose is a reducing sugar. All reducing sugar undergo mutarotation in aqueous solution. The equilibrium mixture at 20 °C is composed of 62.7 % β-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-glucopyranose) and 37.3 % α-lactose (β-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→4)-α-D-glucopyranose).
polysaccharide → polisaharid
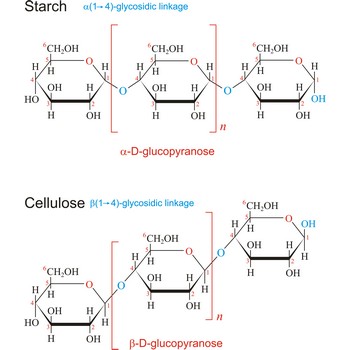
Polysaccharides are compounds consisting of a large number of simple sugars (monosaccharides) linked together by glycosidic bonds. When polysaccharides are composed of a single monosaccharide building block, they are termed homopolysaccharides. Heteropolysaccharides contain two or more different types of monosaccharide. Polysaccharides may have molecular weights of up to several million and are often highly branched. Since they have only the one free anomeric -OH group at the end of a very long chain, polysaccharides aren’t reducing sugars and don’t show noticeable mutarotation. The most common polysaccharides are cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
starch → škrob
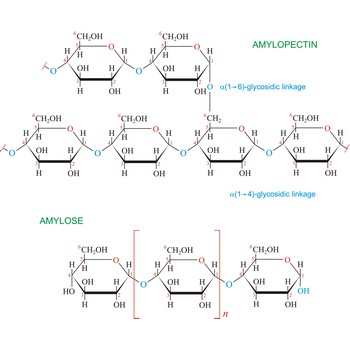
Starch (C6H10O5)x is a polysaccharide used by plants to stockpile glucose molecules. It is the major component of flour, potatoes, rice, beans, corn, and peas. Starch is a mixture of two different polysaccharides: amylose (about 20 %), which is insoluble in cold water, and amylopectin (about 80 %), which is soluble in cold water. Amylose is composed of unbranched chains of D-glucose units joined by α(1→4)-glycosidic linkages. Unlike amylose, which are linear polymers, amylopectin contains α(1→6)-glycoside branches approximately every 25 glucose units.
Starch digestion begins in the mouth via the action of amylase, a digestive enzyme present in saliva. The process is completed in the small intestine by the pancreatic amylase. The final products of starch digestion, glucose molecules, are absorbed into the intestinal bloodstream and transported to the liver. Like most enzymes, glycosidases are highly selective in their action. They hydrolyze only the α-glycoside links in starch and leave the β-glycoside links in cellulose untouched. Starch is important food stuff and is used in adhesives, and sizes, in laundering, pharmacy and medicine.
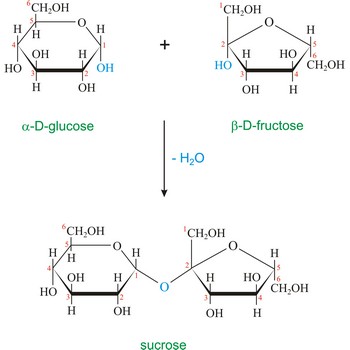
sucrose → saharoza
Sucrose (saccharose), or ordinary table sugar, is a disaccharide in which α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose are joined at their anomeric carbons by a glycosidic bond. There are no hemiacetals remaining in the sucrose and therefore sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation. Sugar is a white crystalline sweet compound found in many plants and extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet. It is used as a sweetening agent in food and drinks. If heated to 200 °C, sucrose becomes caramel. When sucrose is hydrolyzed it forms an equimolar mixture of glucose and fructose. This mixture of monosaccharides is called invert sugar. Honeybees have enzymes called invertases that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose. Honey, in fact, is primarily a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
Chitin → Hitin
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing linear polysaccharide of ß(1->4) linked units of N-acetyl-ß-d-glucosamine. The structure of chitin is similar to cellulose except for the replacement hydroxyl group (-OH) at the carbon 2 with an acetyl amine group (–NH–CO–CH3). Chitin is the main component of the exoskeleton, or outer covering of insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. It is also found in the cell walls of certain fungi and algae. After cellulose, chitin is the second most abundant biopolymer in nature. It is insoluble in water, organic solvents, weak acids and lyes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Glikozid." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table