cysteine → cistein
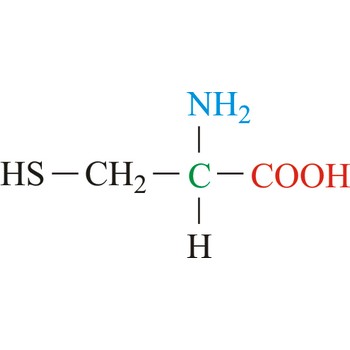
Cysteine is neutral amino acids with polar side chains. Because of its high reactivity, the thiol group of cysteine has numerous biological functions. It serves as a potent nucleophile and metal ligand (particularly for iron and zinc), but is best known for its ability to form disulfide bonds, which often make an important contribution to the stability of extracellular proteins. Cysteine is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans.
- Abbreviations: Cys, C
- IUPAC name: 2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid
- Molecular formula: C3H7NO2S
- Molecular weight: 121.16 g/mol
Daniell cell → Daniellov članak
In 1836 the British chemist John Frederic Daniell (1790-1845) proposed an improved electric cell that supplied an even current during continuous operation. Daniell cell consisted of a glass jar containing copper and zinc electrodes, each immersed in their respective acidic sulphate solutions. The two solutions were separated by a porous clay cylinder separator. It was a galvanic cell in which the spontaneous electrodissolution of zinc and electroplating of copper provided the electrical current.
Zn(s) |
→ | Zn2+ + 2e- |
+0.763 V |
Cu2+ + 2e- |
→ | Cu(s) |
+0.337 V |
Zn(s) + Cu2+ |
→← | Zn2+ + Cu(s) |
+1.100 V |
decay series → raspadni niz
Decay series is a series of decay in which radioactive element is decomposed in different elements until it produces one stable atom.
desiccator → eksikator
Desiccator is a glass container with dry atmosphere due to the presence of some dehydrating agent. It is used for protecting the samples, reagents or precipitates from humidity. As dehydrating agent usually waterless calcium chloride (CaCl2) is used.
diamond → dijamant
Diamond is the hardest known mineral (with a hardness of 10 on Mohs’ scale). It is an allotropic form of pure carbon that has crystallised in the cubic system, usually as octahedral or cubes, under great pressure. Diamond crystals my be colourless and transparent or yellow, brown or black. They are highly prized as gemstones, but also have extensive uses in industry, mainly for cutting and grinding tools. Diamonds occur in ancient volcanic pipes of kimberlite, or in river deposits that have been derived from weathered kimberlite. Industrial diamonds are being increasingly synthetically produced.
diffraction → difrakcija
Diffraction is the ability of a wave to bend around the edges of obstacles or holes. The effect is most noticeable when the obstacle or hole is comparable to the size of the wavelength
dioxin → dioksin
Dioxin is a general term that describes a group of hundreds of chemicals that are highly persistent in the environment. The most toxic compound is 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin or TCDD. The toxicity of other dioxins and chemicals like PCBs that act like dioxin are measured in relation to TCDD. Dioxin is formed as an unintentional by-product of many industrial processes involving chlorine such as waste incineration, chemical and pesticide manufacturing and pulp and paper bleaching. Dioxin was the primary toxic component of Agent Orange, found at Love Canal in Niagara Falls, NY and was the basis for evacuations at Times Beach, MO and Seveso, Italy.
Dioxin is formed by burning chlorine-based chemical compounds with hydrocarbons. The major source of dioxin in the environment comes from waste-burning incinerators of various sorts and also from backyard burn-barrels. Dioxin pollution is also affiliated with paper mills which use chlorine bleaching in their process, with the production of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) plastics, and with the production of certain chlorinated chemicals (like many pesticides).
dipole molecule → dipolna molekula
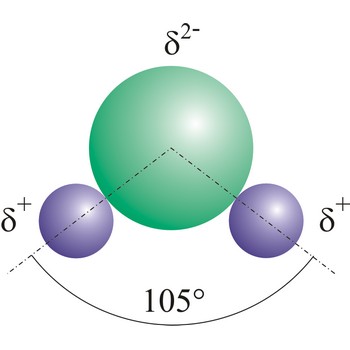
Dipole molecules are created when mutual electronic pair at covalent bond is asymmetrical. If different atoms are bonded by a covalent bond, which can have different electron affinity, then the the atom with greater electron affinity will attract the electron pairs more strongly. In this way an asymmetrical distribution of negative charge appears in a molecule, so one part of the molecule becomes relatively negatively (the one closer to the electron pair) and the other becomes relatively positively charged.
disaccharide → disaharid
Disaccharides are compounds in which two monosaccharides are joined by a glycosidic bond. A glycosidic bond to the anomeric carbon can be either α or β. For example, maltose, the disaccharide obtained by enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of starch, consists of two D-glucopyranose units joined by a 1,4’-α-glycoside bond. The "prime" superscript indicates that C-4 is not in the same ring as C-1. Unlike the other disaccharides, sucrose is not a reducing sugar and does not exhibit mutarotation because the glycosidic bond is between the anomeric carbon of glucose and the anomeric carbon of fructose.
distillation → destilacija
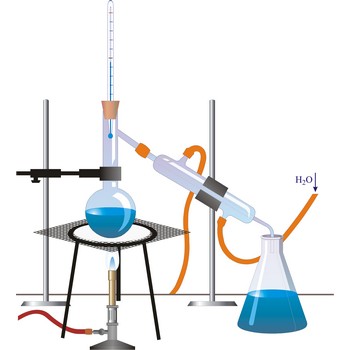
Distillation is a process of boiling a liquid and condensing and collecting the vapour. The liquid collected is the distillate. The usual purpose of distillation is purification or separation of the components of a mixture. This is possible because the composition of the vapour is usually different from that of liquid mixture from which it is obtained. Petrol, kerosene, fuel oil, and lubricating oil are produced from petroleum by distillation.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Gallery/images.php." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table