bioelement → bioelement
Bioelement is any chemical element that is found in the molecules and compounds that make up living organism.
alkaline earth metal → zemnoalkalijski metal
Alkali earth metal is a term that refers to six elements: beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). These elements make up group 2 of the periodic table of elements. They all exhibit a single oxidation state, +2. They are all light and very reactive. Barium and radium are the most reactive and beryllium is the least.
To denote slightly soluble metal oxides chemists formerly used the term "earth". The oxides of barium, strontium, and calcium resemble alumina (Al2O3), a typical "earth", but form alkaline mixtures with water. For this reason barium, strontium, and calcium were called alkaline earth metals. This name has now been extended to include all of the elements of group 2.
allotrope → alotrop
Allotropes are the elements which exist in two or more different forms in the same physical state. Allotropes generally differ in physical properties and may also differ in chemical activity.
Diamond, graphite and fullerenes are three allotropes of the element carbon. Graphite is a soft, black, slippery substance; by contrast, diamond is one of the hardest substances known. The different properties of the allotropes arise from their chemical structures. Diamonds typically crystallize in the cubic crystal system and consist of tetrahedrally bonded carbon atoms. Graphite crystallizes in the hexagonal system. In the fullerenes, the carbon atoms taking the form of a hollow sphere, ellipsoid, or tube.
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C.
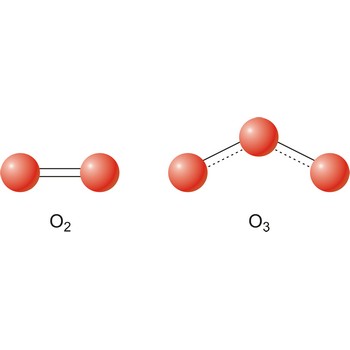
The term allotropes may also be used to refer to the molecular forms of an element. Ozone is a chemically active triatomic allotrope of the element oxygen.
allotropic modification → alotropska modifikacija
Different substances of the same elementary system are called allotropes or allotropic modifications. In the case of oxygen, there are two allotropic modifications: "normal" dioxygen (O2) and trioxygen (O3) or ozone.
chalcogens → halkogeni elementi
Chalcogens are the Group 16 elements: oxygen (O), sulphur (S), selenium Se), tellurium (Te), and polonium (Po). Compounds of these elements are called chalcogenides.
chemical equation equalization → izjednačavanje kemijske jednadžbe
Chemical equation equalization is determining values of stechiometric coefficients of reactants and products in a chemical equation in a way that the number of atoms of each element is equal before and after the reaction.
allotropy → alotropija
Allotropy (Gr. allos, other, and tropos, manner) is the phenomenon of an element existing in two or more physical forms in the same physical state. The difference between the forms involves either crystaline structure (white, red and black phosphorus), the number of atoms in the molecule of a gas (diatomic oxygen and triatomic ozone), or the molecular structure of a liquid (liquid helium an helium II).
In some cases, the allotropes are stable over a temperature range, with a definite transition point at which one changes into the other. For instance, tin has two allotropes: white (metallic) tin stable above 13.2 °C and grey (nonmetallic) tin stable below 13.2 °C. This form allotropy is called enantiotropy. Form of allotropy, in which there is no transition temperature at which the two are in equilibrium, is called monotropy.
Allotropy does not apply to the substance existing in different physical states as, for example, when ice melts and changes from solid ice to liquid water.
Allotropy is generally restricted to describing polymorphic behaviour in elements, while polymorphism may refer to any material having multiple crystal structures.
alpha particle → alfa-čestica
Alpha particle is a helium nucleus emitted spontaneously from radioactive elements, both natural and manufactured. Its energy is in range 4-8 MeV and is dissipated in a very short path, i.e. a few centimetres of air or less than 0.005 mm of aluminium. As helium nucleus consists of two protons and two neutrons bound together as a stable entity the loss of an alpha particle involves a decrease in nucleon number of 4 and decrease of 2 in the atomic number, e.g.
A stream of alpha particles is known as an alpha ray or alpha-radiation.
aluminium → aluminij
Aluminium was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler (Germany) in 1827. The origin of the name comes from the Latin word alumen meaning alum. It is soft, lightweight, silvery-white metal. Exposed surfaces quickly form protective oxide coating. Metal reacts violently with oxidants. Third most abundant element in the earth’s crust. Aluminium is the most abundant metal to be found in the earth’s crust, but is never found free in nature. Aluminium is obtained by electrolysis from bauxite. Used for many purposes from airplanes to beverage cans. Too soft in its pure form so less than 1 % of silicon or iron is added, which hardens and strengthens it.
chemical symbols → kemijski simboli
Chemical symbols are a derived way of showing elements in a formula or equation. Each symbol represents one atom and it usually consists of the first two letters of the Greek or Latin name of the element.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Elementi rijetkih zemalja." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table