alkynes → alkini
Alkynes (acetylenes) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one or more triple carbon-carbon bond. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkyne names end in the suffix -yne. The general formula is CnH(2n+2)-4x were x is the number of triple bonds. Alkynes that have only one triple bond form a homologous series: ethyne (acetylene), CH≡CH, propyne, CH3CH≡CH, etc. Like alkenes, alkynes undergo addition reaction.
Allihn condenser → Allihnovo hladilo
Allihn condenser or bulb condenser consists of an outer water jacket and the inner glass tube with a series of spherical bubbles to maximize the thermal contact with the cooling water. It is named after its inventor, the German chemist Felix Richard Allihn (1854-1915).
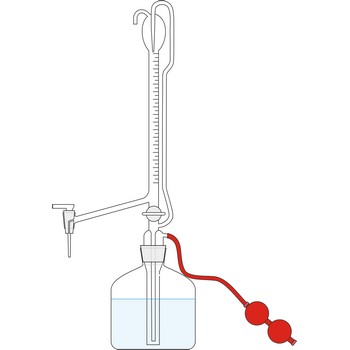
automatic burette → automatska bireta
Automatic burette is used for series of tests. It is connected with a bottle which contains the titration solution. The air is pumped into the bottle by a small rubber air pump, created the pressure in the bottle which the rises the solution to the top of burette. When the the burette is full, the valve is released, the pressure in the bottle falls and the burette automatically sets itself to zero. Work with automatic burettes is by far faster and the consumption of standard solution is smaller.
diffraction grating → difrakcijska rešetka
Diffraction grating is a series of slits used to separate an incident wave into its component wavelengths by directionally separating their diffraction maxima.
battery → baterija
Battery a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. The process underlying the operation of a battery involves a chemical reaction in which electrons are transferred from one chemical species to another. This process is carried out in two half-reactions, one that involves the loss of electrons and one that involves their gain. The battery is an electrochemical cell divided in two half-cells, and reaction proceeds when these are connected together by an electrically conducting pathway. The passage of electrons from one half-cell to the other corresponds to an electric current. Each half-cell contains an electrode in contact with the reacting species. The electrode which passes electrons into the circuit when battery discharges is called anode and is negative terminal. The electrode which receives electrons is called cathode, and is the battery’s positive terminal. The electrical circuit is completed by an electrolyte, an electrically conducting substance placed between the two electrodes which carriers a flow of charge between them. In wet cells, the electrolyte is a liquid containing dissolved ions, whose motion generates an electrical current; in dry cells the electrolyte is basely solid, for example, a solid with mobile ions or porous solid saturated with an ionic solution.
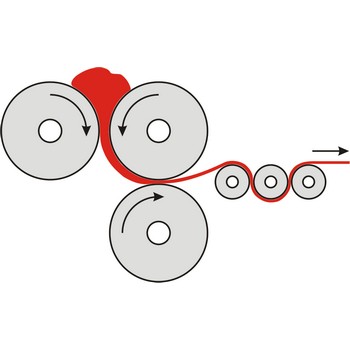
calendering → kalandriranje
Calendering is the process of forming materials to make a film/sheet by passing them through a series of hot rollers.
electron volt → elektronvolt
Electron volt (eV) is a non-SI unit of energy used in atomic and nuclear physics, equal to approximately 1.602 177×10-19 J. The electron volt is defined as the kinetic energy acquired by an electron upon acceleration through a potential difference of 1 V.
farad → farad
Farad (F) is the SI derived unit of electric capacitance. The farad is the capacitance of an electric capacitor between the two plates of which there appears a difference of electric potential of one volt when it is charged by a quantity of electricity equal to one coulomb (F = C/V). The unit was named after the British scientist M. Faraday (1791-1867).
Born-Haber cycle → Born-Haberov kružni proces
Born-Haber cycle is a cycle of reactions used for calculating the lattice energies of ionic crystalline solids. For a compound MX, the lattice energy is the enthalpy of the reaction
The standard enthalpy of formation of the ionic solid is the enthalpy of the reaction
The cycle involves equating this enthalpy (which can be measured) to the sum of the enthalpies of a number of steps proceeding from the elements to the ionic solid. The steps are:
1) Atomization of the metal
2) Atomization of the nonmetal
3) Ionisation of the metal
This is obtained from the ionisation potential.
4) Ionisation of the nonmetal
This is electron affinity.
5) Formation of the ionic solids
Equation of the enthalpies gives
from which ΔHL can be found.
cathode → katoda
Cathode is a negative electrode of an electrolytic cell to which positively charged ions (cations) migrate when a current is passed as in electroplating baths.
In a primary or secondary cell (battery or accumulator) the cathode is the electrode that spontaneously becomes negative during discharge, and form which therefore electrons emerge.
In vacuum electronic devices electrons are emitted by the cathode and flow to the anode.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Electrode potential series." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table