Results 1–3 of 3 for barometar
barometer → barometar
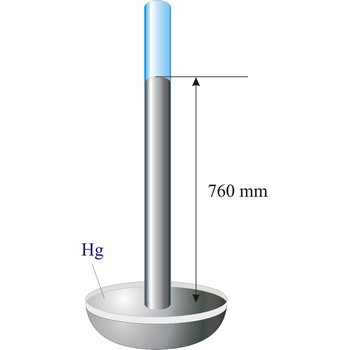
Barometer is an instrument that measures atmospheric pressure. A mercury barometer is a closed tube filled with mercury inverted in a mercury reservoir. The height of the mercury column indicates atmospheric pressure (with 1 atm = 760 mm of mercury). An aneroid barometer consists of an evacuated container with a flexible wall. When atmospheric pressure changes, the wall flexes and moves a pointer which indicates the changing pressure on a scale.
Torricelli, Evangelista → Torricelli, Evangelista
Evangelista Torricelli (1852-1908) is Italian physicist and mathematician. He became the first scientist to create a sustained vacuum and to discover the principle of a barometer. He filled a tube three feet long, and hermetically closed at one end, with mercury and set it vertically with the open end in a basin of mercury, taking care that no air-bubbles should get into the tube. The column of mercury invariably fell to about twenty-eight inches, leaving an empty space above its level. He discovered that the variation of the height of the mercury from day to day was caused by changes in the atmospheric pressure. He also constructed a number of large objectives and small, short focus, simple microscopes.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Barometar." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table