alkanes → alkani
Alkanes (paraffins) are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2, and therefore consisting entirely of hydrogen atoms and saturated carbon atoms. In the systematic chemical nomenclature alkane names end in the suffix -ane. They form a homologous series (the alkane series) methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), etc. The lower members of the series are gases; the high-molecular mass alkanes are waxy solid. Generaly the alkanes are fairly unreactive. They form haloalkanes with halogens when irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. Alkanes are present in natural gas and petroleum.
calorimetry → kalorimetrija
Calorimetry is a measurement of the amount of heat evolved or absorbed in a chemical reaction, change of state, or formation of a solution, or any other event that includes heat transfer.
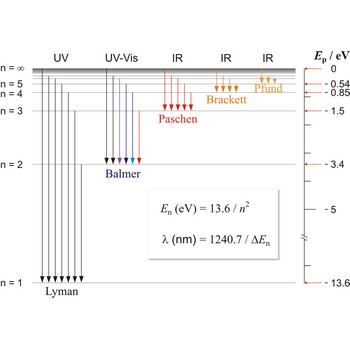
Balmer series → Balmerova serija
Balmer series, Balmer lines is a series of lines in the emission spectrum of hydrogen that involve transitions to the n=2 state from states with n>2.
Bohr atom → Bohrov atom
Bohr atom is a model of the atom that explains emission and absorption of radiation as transitions between stationary electronic states in which the electron orbits the nucleus at a definite distance. The Bohr model violates the Heisenberg uncertainty principle since it postulates definite paths and moment for electrons as they move around the nucleus. Modern theories usually use atomic orbitals to describe the behaviour of electrons in atoms.
Born-Haber cycle → Born-Haberov kružni proces
Born-Haber cycle is a cycle of reactions used for calculating the lattice energies of ionic crystalline solids. For a compound MX, the lattice energy is the enthalpy of the reaction
The standard enthalpy of formation of the ionic solid is the enthalpy of the reaction
The cycle involves equating this enthalpy (which can be measured) to the sum of the enthalpies of a number of steps proceeding from the elements to the ionic solid. The steps are:
1) Atomization of the metal
2) Atomization of the nonmetal
3) Ionisation of the metal
This is obtained from the ionisation potential.
4) Ionisation of the nonmetal
This is electron affinity.
5) Formation of the ionic solids
Equation of the enthalpies gives
from which ΔHL can be found.
fluorescence → fluorescencija
Fluorescence is a luminescence phenomenon in which electron returns to it's ground state almost instantaneously (less than 10-8 second), and in which emission from a luminescent substance ceases when the exciting source is removed. Fluorescence is characterized by radiation emission in all directions.
Carnot cycle → Carnotov kružni proces
Carnot cycle is the most efficient cycle of operations for a reversible heat engine. Published in 1824 by French physicist Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), it consists of four operations on the working substance in the engine:
1-2: Isothermal expansion at thermodynamic temperature T1 with heat QH taken in.
2-3: Adiabatic expansion with a fall of temperature to T2.
3-4: Isothermal compression at temperature T2 with heat QC given out.
4-1: Adiabatic compression at temperature back to T1.
According to the Carnot principle, the efficiency of any reversible heat engine depends only on the temperature range through which it works, rather than the properties of the working substances.
cellulose → celuloza
Cellulose, (C6H10O5)n, is a polysaccharide that consists of a long unbranched chain of glucose units linked by (1→4)-β-glycoside bonds. Nature uses cellulose primarily as a structural material to impart strength and rigidity to plants. Leaves, grasses, and cotton are primarily cellulose. The fibrous nature of extracted cellulose has led to its use in textile industry for the production of cotton, artificial silk, etc. Cellulose also serves as raw material for the manufacture of cellulose acetate, known commercially as acetate rayon, and cellulose nitrate, known as guncotton. Gunncotton is the major ingredient in smokeless powder, the explosive propellant used in artillery shells and in ammunition for firearms.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Agregatno stanje." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table