heat of fusion → toplina taljenja
Heat of fusion or enthalpy of fusion is the heat required to convert a substance from the solid to the liquid state with no temperature change (also called latent heat of fusion or melting).
heat of sublimation → toplina sublimacije
Heat of sublimation or enthalpy of sublimation is the energy required to convert one mole of a substance from the solid to the gas state (sublimation) without the appearance of the liquid state.
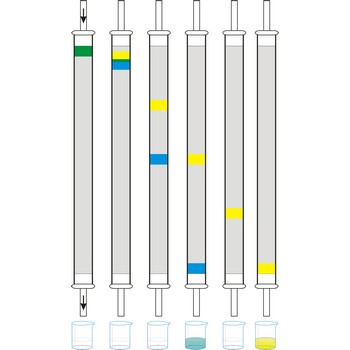
column chromatography → kromatografija u koloni
Column chromatography is generally used as a purification technique: it isolates desired compounds from a mixture. In column chromatography, the stationary phase, a solid adsorbent, is placed in a vertical column. The mobile phase, a liquid, is added to the top and flows down through the column by either gravity or external pressure. The mobile phase can be a gas or a liquid which gives rise to the two basic forms of chromatography, namely, gas chromatography (GC) and liquid chromatography (LC).
condensation → kondenzacija
1. Condensation is a process of changing from a gaseous to a liquid or solid state, usually done by cooling.
2. Condensation, in colloid systems, is a process where smaller particle join in one colloid size particle
3. Condensation, in chemical terms, is a sort of chemical reaction in which small molecules like water, carbon dioxide, or ammonia single out.
heterogenic reaction → heterogena reakcija
Heterogenic reactions are those reactions which take place in different phases (in different aggregate states).
homogenic reaction → homogena reakcija
Homogenic reactions are those reactions in which products and reactants are in the same phase (aggregate state).
critical temperature → kritična temperatura
Critical temperature is the temperature of the liquid-vapour critical point, that is, the temperature above which a gas cannot be liquefied by an increase of pressure.
latent heat → latentna toplina
Latent heat (L) is the quantity of heat absorbed or released when a substance changes its physical phase at constant temperature (e.g. from solid to liquid at the melting point or from liquid to gas at the boiling point).
gas → plin
Gas is a state of matter, in which the mollecules move freely and consequently the entire mass tends to expand indefinitely, occupying the total volume of any vessel into which it is introduced. Gases follow, within considerable degree of fidelity, certain laws relating their conditions of pressure, volume and temperature. Gases mix freely with each other, and they can be liquefied through compression or temperature reduction.
Citing this page:
Generalic, Eni. "Agregatno stanje." Croatian-English Chemistry Dictionary & Glossary. 29 June 2022. KTF-Split. {Date of access}. <https://glossary.periodni.com>.
Glossary
Periodic Table